a class to store JSON values More...
#include <json.hpp>
 Collaboration diagram for nlohmann::basic_json:
Collaboration diagram for nlohmann::basic_json:Public Types | |
| using | cbor_tag_handler_t = detail::cbor_tag_handler_t |
| how to treat CBOR tags More... | |
| using | error_handler_t = detail::error_handler_t |
| how to treat decoding errors More... | |
| using | initializer_list_t = std::initializer_list< detail::json_ref< basic_json > > |
| helper type for initializer lists of basic_json values More... | |
| using | input_format_t = detail::input_format_t |
| using | json_pointer = ::nlohmann::json_pointer< basic_json > |
| JSON Pointer, see nlohmann::json_pointer. More... | |
| using | json_sax_t = json_sax< basic_json > |
| SAX interface type, see nlohmann::json_sax. More... | |
| template<typename T , typename SFINAE > | |
| using | json_serializer = JSONSerializer< T, SFINAE > |
| using | parse_event_t = detail::parse_event_t |
| parser event types More... | |
| using | parser_callback_t = detail::parser_callback_t< basic_json > |
| per-element parser callback type More... | |
| using | value_t = detail::value_t |
Public Member Functions | |
| const JSON_HEDLEY_RETURNS_NON_NULL char * | type_name () const noexcept |
| return the type as string More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static allocator_type | get_allocator () |
| returns the allocator associated with the container More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | meta () |
| returns version information on the library More... | |
Data Fields | |
| JSON_PRIVATE_UNLESS_TESTED | __pad3__: value_t m_type = value_t::null |
| json_value | m_value = {} |
| the value of the current element More... | |
Private Types | |
| using | basic_json_t = NLOHMANN_BASIC_JSON_TPL |
| workaround type for MSVC More... | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| using | binary_reader = ::nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< basic_json, InputType > |
| template<typename CharType > | |
| using | binary_writer = ::nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< basic_json, CharType > |
| template<typename BasicJsonType > | |
| using | internal_iterator = ::nlohmann::detail::internal_iterator< BasicJsonType > |
| template<typename BasicJsonType > | |
| using | iter_impl = ::nlohmann::detail::iter_impl< BasicJsonType > |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| using | iteration_proxy = ::nlohmann::detail::iteration_proxy< Iterator > |
| template<typename Base > | |
| using | json_reverse_iterator = ::nlohmann::detail::json_reverse_iterator< Base > |
| template<typename CharType > | |
| using | output_adapter_t = ::nlohmann::detail::output_adapter_t< CharType > |
| using | primitive_iterator_t = ::nlohmann::detail::primitive_iterator_t |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | assert_invariant (bool check_parents=true) const noexcept |
| checks the class invariants More... | |
| void | destroy (value_t t) |
| boolean_t | get_impl (boolean_t *) const |
| get a boolean (explicit) More... | |
| array_t * | get_impl_ptr (array_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (array) More... | |
| binary_t * | get_impl_ptr (binary_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (binary) More... | |
| boolean_t * | get_impl_ptr (boolean_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (boolean) More... | |
| constexpr const array_t * | get_impl_ptr (const array_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (array) More... | |
| constexpr const binary_t * | get_impl_ptr (const binary_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (binary) More... | |
| constexpr const boolean_t * | get_impl_ptr (const boolean_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (boolean) More... | |
| constexpr const number_float_t * | get_impl_ptr (const number_float_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (floating-point number) More... | |
| constexpr const number_integer_t * | get_impl_ptr (const number_integer_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (integer number) More... | |
| constexpr const number_unsigned_t * | get_impl_ptr (const number_unsigned_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (unsigned number) More... | |
| constexpr const object_t * | get_impl_ptr (const object_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (object) More... | |
| constexpr const string_t * | get_impl_ptr (const string_t *) const noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (string) More... | |
| number_float_t * | get_impl_ptr (number_float_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (floating-point number) More... | |
| number_integer_t * | get_impl_ptr (number_integer_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (integer number) More... | |
| number_unsigned_t * | get_impl_ptr (number_unsigned_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (unsigned number) More... | |
| object_t * | get_impl_ptr (object_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (object) More... | |
| string_t * | get_impl_ptr (string_t *) noexcept |
| get a pointer to the value (string) More... | |
| json_value ()=default | |
| default constructor (for null values) More... | |
| json_value (array_t &&value) | |
| constructor for rvalue arrays More... | |
| json_value (binary_t &&value) | |
| constructor for rvalue binary arrays (internal type) More... | |
| json_value (boolean_t v) noexcept | |
| constructor for booleans More... | |
| json_value (const array_t &value) | |
| constructor for arrays More... | |
| json_value (const binary_t &value) | |
| constructor for binary arrays (internal type) More... | |
| json_value (const object_t &value) | |
| constructor for objects More... | |
| json_value (const string_t &value) | |
| constructor for strings More... | |
| json_value (const typename binary_t::container_type &value) | |
| constructor for binary arrays More... | |
| json_value (number_float_t v) noexcept | |
| constructor for numbers (floating-point) More... | |
| json_value (number_integer_t v) noexcept | |
| constructor for numbers (integer) More... | |
| json_value (number_unsigned_t v) noexcept | |
| constructor for numbers (unsigned) More... | |
| json_value (object_t &&value) | |
| constructor for rvalue objects More... | |
| json_value (string_t &&value) | |
| constructor for rvalue strings More... | |
| json_value (typename binary_t::container_type &&value) | |
| constructor for rvalue binary arrays More... | |
| json_value (value_t t) | |
| constructor for empty values of a given type More... | |
| template<typename InputAdapterType > | |
| static ::nlohmann::detail::parser< basic_json, InputAdapterType > | parser (InputAdapterType adapter, detail::parser_callback_t< basic_json >cb=nullptr, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| reference | set_parent (reference j, std::size_t old_capacity=std::size_t(-1)) |
| void | set_parents () |
| iterator | set_parents (iterator it, typename iterator::difference_type count) |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| template<typename T , typename... Args> | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_RETURNS_NON_NULL T * | create (Args &&... args) |
| helper for exception-safe object creation More... | |
| template<typename ReferenceType , typename ThisType > | |
| static ReferenceType | get_ref_impl (ThisType &obj) |
| helper function to implement get_ref() More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| JSON_PRIVATE_UNLESS_TESTED | __pad0__: using lexer = ::nlohmann::detail::lexer_base<basic_json> |
| JSON_PRIVATE_UNLESS_TESTED | __pad1__: using serializer = ::nlohmann::detail::serializer<basic_json> |
| JSON_PRIVATE_UNLESS_TESTED | __pad2__: union json_value { object_t* object |
| array_t * | array |
| array (stored with pointer to save storage) More... | |
| binary_t * | binary |
| binary (stored with pointer to save storage) More... | |
| boolean_t | boolean |
| boolean More... | |
| number_float_t | number_float |
| number (floating-point) More... | |
| number_integer_t | number_integer |
| number (integer) More... | |
| number_unsigned_t | number_unsigned |
| number (unsigned integer) More... | |
| string_t * | string |
| string (stored with pointer to save storage) More... | |
Friends | |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , typename InputType , typename SAX > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::binary_reader |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , typename CharType > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::binary_writer |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::exception |
| template<typename BasicJsonType > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::iter_impl |
| template<typename BasicJsonType > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::json_sax_dom_callback_parser |
| template<typename BasicJsonType > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::json_sax_dom_parser |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , typename InputType > | |
| class | ::nlohmann::detail::parser |
| template<detail::value_t > | |
| struct | detail::external_constructor |
exceptions | |
| using | exception = detail::exception |
| general exception of the basic_json class More... | |
| using | parse_error = detail::parse_error |
| exception indicating a parse error More... | |
| using | invalid_iterator = detail::invalid_iterator |
| exception indicating errors with iterators More... | |
| using | type_error = detail::type_error |
| exception indicating executing a member function with a wrong type More... | |
| using | out_of_range = detail::out_of_range |
| exception indicating access out of the defined range More... | |
| using | other_error = detail::other_error |
| exception indicating other library errors More... | |
container types | |
The canonic container types to use basic_json like any other STL container. | |
| using | value_type = basic_json |
| the type of elements in a basic_json container More... | |
| using | reference = value_type & |
| the type of an element reference More... | |
| using | const_reference = const value_type & |
| the type of an element const reference More... | |
| using | difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t |
| a type to represent differences between iterators More... | |
| using | size_type = std::size_t |
| a type to represent container sizes More... | |
| using | allocator_type = AllocatorType< basic_json > |
| the allocator type More... | |
| using | pointer = typename std::allocator_traits< allocator_type >::pointer |
| the type of an element pointer More... | |
| using | const_pointer = typename std::allocator_traits< allocator_type >::const_pointer |
| the type of an element const pointer More... | |
| using | iterator = iter_impl< basic_json > |
| an iterator for a basic_json container More... | |
| using | const_iterator = iter_impl< const basic_json > |
| a const iterator for a basic_json container More... | |
| using | reverse_iterator = json_reverse_iterator< typename basic_json::iterator > |
| a reverse iterator for a basic_json container More... | |
| using | const_reverse_iterator = json_reverse_iterator< typename basic_json::const_iterator > |
| a const reverse iterator for a basic_json container More... | |
JSON value data types | |
The data types to store a JSON value. These types are derived from the template arguments passed to class basic_json. | |
| using | object_comparator_t = std::less< StringType > |
| using | object_t = ObjectType< StringType, basic_json, object_comparator_t, AllocatorType< std::pair< const StringType, basic_json > >> |
| a type for an object More... | |
| using | array_t = ArrayType< basic_json, AllocatorType< basic_json > > |
| a type for an array More... | |
| using | string_t = StringType |
| a type for a string More... | |
| using | boolean_t = BooleanType |
| a type for a boolean More... | |
| using | number_integer_t = NumberIntegerType |
| a type for a number (integer) More... | |
| using | number_unsigned_t = NumberUnsignedType |
| a type for a number (unsigned) More... | |
| using | number_float_t = NumberFloatType |
| a type for a number (floating-point) More... | |
| using | binary_t = nlohmann::byte_container_with_subtype< BinaryType > |
| a type for a packed binary type More... | |
constructors and destructors | |
Constructors of class basic_json, copy/move constructor, copy assignment, static functions creating objects, and the destructor. | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | binary (const typename binary_t::container_type &init) |
| explicitly create a binary array (without subtype) More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | binary (const typename binary_t::container_type &init, typename binary_t::subtype_type subtype) |
| explicitly create a binary array (with subtype) More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | binary (typename binary_t::container_type &&init) |
| explicitly create a binary array (without subtype) More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | binary (typename binary_t::container_type &&init, typename binary_t::subtype_type subtype) |
| explicitly create a binary array (with subtype) More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | array (initializer_list_t init={}) |
| explicitly create an array from an initializer list More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | object (initializer_list_t init={}) |
| explicitly create an object from an initializer list More... | |
| basic_json (const value_t v) | |
| create an empty value with a given type More... | |
| basic_json (std::nullptr_t=nullptr) noexcept | |
| create a null object More... | |
| template<typename CompatibleType , typename U = detail::uncvref_t<CompatibleType>, detail::enable_if_t< !detail::is_basic_json< U >::value &&detail::is_compatible_type< basic_json_t, U >::value, int > = 0> | |
| basic_json (CompatibleType &&val) noexcept(noexcept(//NOLINT(bugprone-forwarding-reference-overload, bugprone-exception-escape) JSONSerializer< U >::to_json(std::declval< basic_json_t & >(), std::forward< CompatibleType >(val)))) | |
| create a JSON value More... | |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , detail::enable_if_t< detail::is_basic_json< BasicJsonType >::value &&!std::is_same< basic_json, BasicJsonType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| basic_json (const BasicJsonType &val) | |
| create a JSON value from an existing one More... | |
| basic_json (initializer_list_t init, bool type_deduction=true, value_t manual_type=value_t::array) | |
| create a container (array or object) from an initializer list More... | |
| basic_json (size_type cnt, const basic_json &val) | |
| construct an array with count copies of given value More... | |
| template<class InputIT , typename std::enable_if< std::is_same< InputIT, typename basic_json_t::iterator >::value||std::is_same< InputIT, typename basic_json_t::const_iterator >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| basic_json (InputIT first, InputIT last) | |
| construct a JSON container given an iterator range More... | |
| template<typename JsonRef , detail::enable_if_t< detail::conjunction< detail::is_json_ref< JsonRef >, std::is_same< typename JsonRef::value_type, basic_json >>::value, int > = 0> | |
| basic_json (const JsonRef &ref) | |
| basic_json (const basic_json &other) | |
| copy constructor More... | |
| basic_json (basic_json &&other) noexcept | |
| move constructor More... | |
| basic_json & | operator= (basic_json other) noexcept(std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< json_value >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< json_value >::value) |
| copy assignment More... | |
| ~basic_json () noexcept | |
| destructor More... | |
object inspection | |
| string_t | dump (const int indent=-1, const char indent_char=' ', const bool ensure_ascii=false, const error_handler_t error_handler=error_handler_t::strict) const |
| serialization More... | |
| constexpr value_t | type () const noexcept |
| return the type of the JSON value (explicit) More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_primitive () const noexcept |
| return whether type is primitive More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_structured () const noexcept |
| return whether type is structured More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_null () const noexcept |
| return whether value is null More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_boolean () const noexcept |
| return whether value is a boolean More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_number () const noexcept |
| return whether value is a number More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_number_integer () const noexcept |
| return whether value is an integer number More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_number_unsigned () const noexcept |
| return whether value is an unsigned integer number More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_number_float () const noexcept |
| return whether value is a floating-point number More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_object () const noexcept |
| return whether value is an object More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_array () const noexcept |
| return whether value is an array More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_string () const noexcept |
| return whether value is a string More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_binary () const noexcept |
| return whether value is a binary array More... | |
| constexpr bool | is_discarded () const noexcept |
| return whether value is discarded More... | |
| constexpr | operator value_t () const noexcept |
| return the type of the JSON value (implicit) More... | |
value access | |
| template<typename ValueType , detail::enable_if_t< detail::is_default_constructible< ValueType >::value &&detail::has_from_json< basic_json_t, ValueType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| ValueType | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 0 >) const noexcept(noexcept(JSONSerializer< ValueType >::from_json(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >(), std::declval< ValueType & >()))) |
| get a value (explicit) More... | |
| template<typename ValueType , detail::enable_if_t< detail::has_non_default_from_json< basic_json_t, ValueType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| ValueType | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 1 >) const noexcept(noexcept(JSONSerializer< ValueType >::from_json(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >()))) |
| get a value (explicit); special case More... | |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , detail::enable_if_t< detail::is_basic_json< BasicJsonType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| BasicJsonType | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 2 >) const |
| get special-case overload More... | |
| template<typename BasicJsonType , detail::enable_if_t< std::is_same< BasicJsonType, basic_json_t >::value, int > = 0> | |
| basic_json | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 3 >) const |
| get special-case overload More... | |
| template<typename PointerType , detail::enable_if_t< std::is_pointer< PointerType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| constexpr auto | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 4 >) const noexcept -> decltype(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >().template get_ptr< PointerType >()) |
| get a pointer value (explicit) More... | |
| template<typename PointerType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_pointer< PointerType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| auto | get_ptr () noexcept -> decltype(std::declval< basic_json_t & >().get_impl_ptr(std::declval< PointerType >())) |
| get a pointer value (implicit) More... | |
| template<typename PointerType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_pointer< PointerType >::value &&std::is_const< typename std::remove_pointer< PointerType >::type >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| constexpr auto | get_ptr () const noexcept -> decltype(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >().get_impl_ptr(std::declval< PointerType >())) |
| get a pointer value (implicit) More... | |
| template<typename ValueTypeCV , typename ValueType = detail::uncvref_t<ValueTypeCV>> | |
| auto | get () const noexcept(noexcept(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >().template get_impl< ValueType >(detail::priority_tag< 4 > {}))) -> decltype(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >().template get_impl< ValueType >(detail::priority_tag< 4 > |
| get a (pointer) value (explicit) More... | |
| return | get_impl (detail::priority_tag< 4 > {}) |
| template<typename PointerType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_pointer< PointerType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| auto | get () noexcept -> decltype(std::declval< basic_json_t & >().template get_ptr< PointerType >()) |
| get a pointer value (explicit) More... | |
| template<typename ValueType , detail::enable_if_t< !detail::is_basic_json< ValueType >::value &&detail::has_from_json< basic_json_t, ValueType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| ValueType & | get_to (ValueType &v) const noexcept(noexcept(JSONSerializer< ValueType >::from_json(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >(), v))) |
| get a value (explicit) More... | |
| template<typename ValueType , detail::enable_if_t< detail::is_basic_json< ValueType >::value, int > = 0> | |
| ValueType & | get_to (ValueType &v) const |
| template<typename T , std::size_t N, typename Array = T (&)[N], detail::enable_if_t< detail::has_from_json< basic_json_t, Array >::value, int > = 0> | |
| Array | get_to (T(&v)[N]) const noexcept(noexcept(JSONSerializer< Array >::from_json(std::declval< const basic_json_t & >(), v))) |
| template<typename ReferenceType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_reference< ReferenceType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| ReferenceType | get_ref () |
| get a reference value (implicit) More... | |
| template<typename ReferenceType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_reference< ReferenceType >::value &&std::is_const< typename std::remove_reference< ReferenceType >::type >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| ReferenceType | get_ref () const |
| get a reference value (implicit) More... | |
| template<typename ValueType , typename std::enable_if< detail::conjunction< detail::negation< std::is_pointer< ValueType >>, detail::negation< std::is_same< ValueType, detail::json_ref< basic_json >>>, detail::negation< std::is_same< ValueType, typename string_t::value_type >>, detail::negation< detail::is_basic_json< ValueType >>, detail::negation< std::is_same< ValueType, std::initializer_list< typename string_t::value_type >>>, detail::is_detected_lazy< detail::get_template_function, const basic_json_t &, ValueType > >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| JSON_EXPLICIT | operator ValueType () const |
| get a value (implicit) More... | |
| binary_t & | get_binary () |
| const binary_t & | get_binary () const |
element access | |
| reference | at (size_type idx) |
| access specified array element with bounds checking More... | |
| const_reference | at (size_type idx) const |
| access specified array element with bounds checking More... | |
| reference | at (const typename object_t::key_type &key) |
| access specified object element with bounds checking More... | |
| const_reference | at (const typename object_t::key_type &key) const |
| access specified object element with bounds checking More... | |
| reference | operator[] (size_type idx) |
| access specified array element More... | |
| const_reference | operator[] (size_type idx) const |
| access specified array element More... | |
| reference | operator[] (const typename object_t::key_type &key) |
| access specified object element More... | |
| const_reference | operator[] (const typename object_t::key_type &key) const |
| read-only access specified object element More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| reference | operator[] (T *key) |
| access specified object element More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| const_reference | operator[] (T *key) const |
| read-only access specified object element More... | |
| template<class ValueType , typename std::enable_if< detail::is_getable< basic_json_t, ValueType >::value &&!std::is_same< value_t, ValueType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| ValueType | value (const typename object_t::key_type &key, const ValueType &default_value) const |
| access specified object element with default value More... | |
| string_t | value (const typename object_t::key_type &key, const char *default_value) const |
| overload for a default value of type const char* More... | |
| template<class ValueType , typename std::enable_if< detail::is_getable< basic_json_t, ValueType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| ValueType | value (const json_pointer &ptr, const ValueType &default_value) const |
| access specified object element via JSON Pointer with default value More... | |
| string_t | value (const json_pointer &ptr, const char *default_value) const |
| overload for a default value of type const char* More... | |
| reference | front () |
| access the first element More... | |
| const_reference | front () const |
| access the first element More... | |
| reference | back () |
| access the last element More... | |
| const_reference | back () const |
| access the last element More... | |
| template<class IteratorType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_same< IteratorType, typename basic_json_t::iterator >::value||std::is_same< IteratorType, typename basic_json_t::const_iterator >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| IteratorType | erase (IteratorType pos) |
| remove element given an iterator More... | |
| template<class IteratorType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_same< IteratorType, typename basic_json_t::iterator >::value||std::is_same< IteratorType, typename basic_json_t::const_iterator >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| IteratorType | erase (IteratorType first, IteratorType last) |
| remove elements given an iterator range More... | |
| size_type | erase (const typename object_t::key_type &key) |
| remove element from a JSON object given a key More... | |
| void | erase (const size_type idx) |
| remove element from a JSON array given an index More... | |
lookup | |
| template<typename KeyT > | |
| iterator | find (KeyT &&key) |
| find an element in a JSON object More... | |
| template<typename KeyT > | |
| const_iterator | find (KeyT &&key) const |
| find an element in a JSON object More... | |
| template<typename KeyT > | |
| size_type | count (KeyT &&key) const |
| returns the number of occurrences of a key in a JSON object More... | |
| template<typename KeyT , typename std::enable_if< !std::is_same< typename std::decay< KeyT >::type, json_pointer >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | contains (KeyT &&key) const |
| check the existence of an element in a JSON object More... | |
| bool | contains (const json_pointer &ptr) const |
| check the existence of an element in a JSON object given a JSON pointer More... | |
iterators | |
| static iteration_proxy< iterator > | iterator_wrapper (reference ref) noexcept |
| wrapper to access iterator member functions in range-based for More... | |
| static iteration_proxy< const_iterator > | iterator_wrapper (const_reference ref) noexcept |
| wrapper to access iterator member functions in range-based for More... | |
| iterator | begin () noexcept |
| returns an iterator to the first element More... | |
| const_iterator | begin () const noexcept |
| returns a const iterator to the first element More... | |
| const_iterator | cbegin () const noexcept |
| returns a const iterator to the first element More... | |
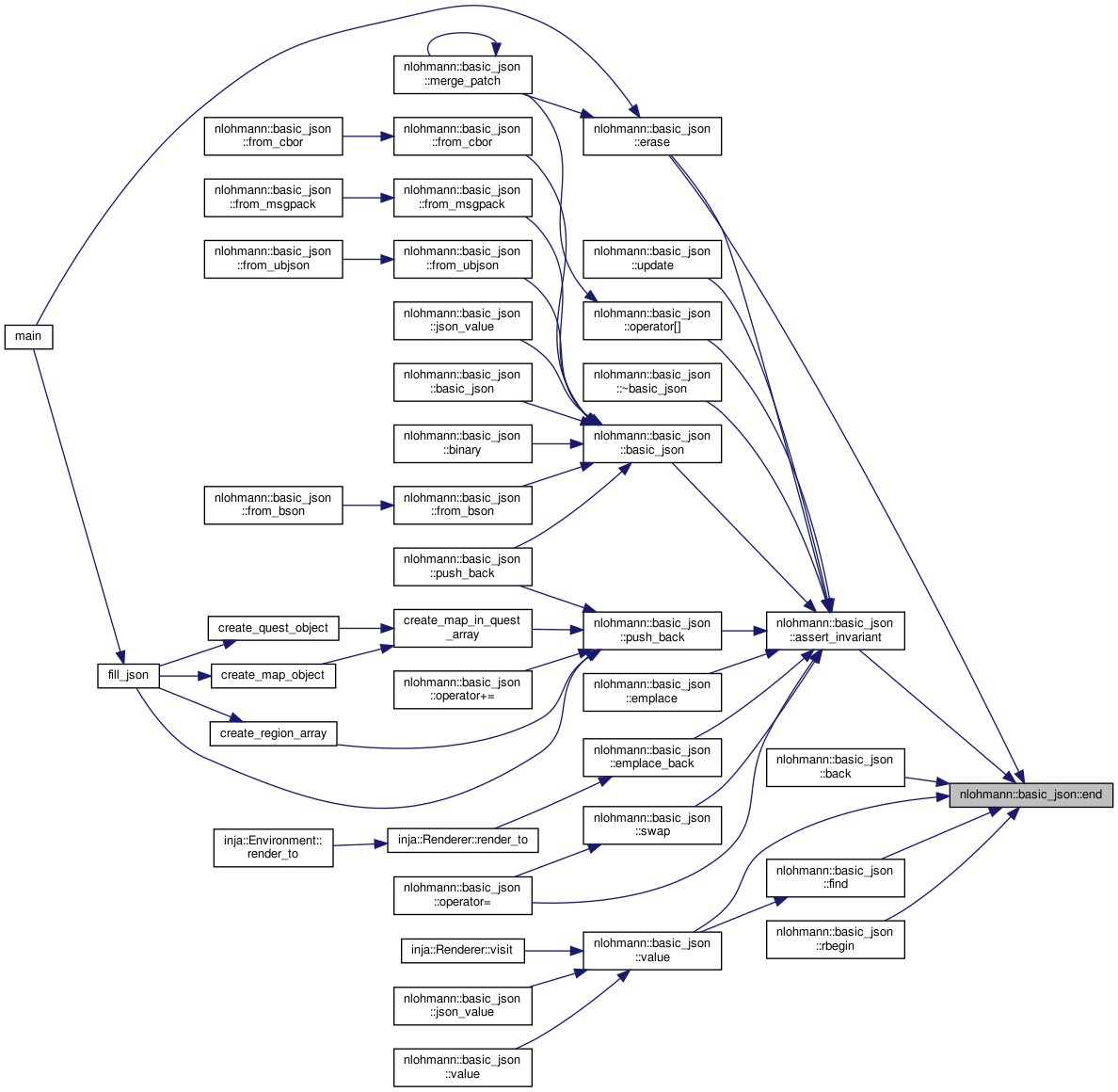
| iterator | end () noexcept |
| returns an iterator to one past the last element More... | |
| const_iterator | end () const noexcept |
| returns a const iterator to one past the last element More... | |
| const_iterator | cend () const noexcept |
| returns a const iterator to one past the last element More... | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () noexcept |
| returns an iterator to the reverse-beginning More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const noexcept |
| returns a const reverse iterator to the last element More... | |
| reverse_iterator | rend () noexcept |
| returns an iterator to the reverse-end More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const noexcept |
| returns a const reverse iterator to one before the first More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crbegin () const noexcept |
| returns a const reverse iterator to the last element More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crend () const noexcept |
| returns a const reverse iterator to one before the first More... | |
| iteration_proxy< iterator > | items () noexcept |
| helper to access iterator member functions in range-based for More... | |
| iteration_proxy< const_iterator > | items () const noexcept |
| helper to access iterator member functions in range-based for More... | |
capacity | |
| bool | empty () const noexcept |
| checks whether the container is empty. More... | |
| size_type | size () const noexcept |
| returns the number of elements More... | |
| size_type | max_size () const noexcept |
| returns the maximum possible number of elements More... | |
modifiers | |
| void | swap (reference left, reference right) noexcept(std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< json_value >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< json_value >::value) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | clear () noexcept |
| clears the contents More... | |
| void | push_back (basic_json &&val) |
| add an object to an array More... | |
| reference | operator+= (basic_json &&val) |
| add an object to an array More... | |
| void | push_back (const basic_json &val) |
| add an object to an array More... | |
| reference | operator+= (const basic_json &val) |
| add an object to an array More... | |
| void | push_back (const typename object_t::value_type &val) |
| add an object to an object More... | |
| reference | operator+= (const typename object_t::value_type &val) |
| add an object to an object More... | |
| void | push_back (initializer_list_t init) |
| add an object to an object More... | |
| reference | operator+= (initializer_list_t init) |
| add an object to an object More... | |
| template<class... Args> | |
| reference | emplace_back (Args &&... args) |
| add an object to an array More... | |
| template<class... Args> | |
| std::pair< iterator, bool > | emplace (Args &&... args) |
| add an object to an object if key does not exist More... | |
| template<typename... Args> | |
| iterator | insert_iterator (const_iterator pos, Args &&... args) |
| iterator | insert (const_iterator pos, const basic_json &val) |
| inserts element More... | |
| iterator | insert (const_iterator pos, basic_json &&val) |
| inserts element More... | |
| iterator | insert (const_iterator pos, size_type cnt, const basic_json &val) |
| inserts elements More... | |
| iterator | insert (const_iterator pos, const_iterator first, const_iterator last) |
| inserts elements More... | |
| iterator | insert (const_iterator pos, initializer_list_t ilist) |
| inserts elements More... | |
| void | insert (const_iterator first, const_iterator last) |
| inserts elements More... | |
| void | update (const_reference j) |
| updates a JSON object from another object, overwriting existing keys More... | |
| void | update (const_iterator first, const_iterator last) |
| updates a JSON object from another object, overwriting existing keys More... | |
| void | swap (reference other) noexcept(std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< value_t >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_constructible< json_value >::value &&std::is_nothrow_move_assignable< json_value >::value) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | swap (array_t &other) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | swap (object_t &other) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | swap (string_t &other) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | swap (binary_t &other) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
| void | swap (typename binary_t::container_type &other) |
| exchanges the values More... | |
lexicographical comparison operators | |
| bool | operator== (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator== (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator== (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: equal More... | |
| bool | operator!= (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: not equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator!= (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: not equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator!= (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: not equal More... | |
| bool | operator< (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator< (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator< (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than More... | |
| bool | operator<= (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than or equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator<= (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than or equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator<= (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: less than or equal More... | |
| bool | operator> (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator> (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator> (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than More... | |
| bool | operator>= (const_reference lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than or equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator>= (const_reference lhs, ScalarType rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than or equal More... | |
| template<typename ScalarType , typename std::enable_if< std::is_scalar< ScalarType >::value, int >::type = 0> | |
| bool | operator>= (ScalarType lhs, const_reference rhs) noexcept |
| comparison: greater than or equal More... | |
serialization | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &o, const basic_json &j) |
| serialize to stream More... | |
| std::ostream & | operator>> (const basic_json &j, std::ostream &o) |
| serialize to stream More... | |
deserialization | |
| std::istream & | operator<< (basic_json &j, std::istream &i) |
| deserialize from stream More... | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &i, basic_json &j) |
| deserialize from stream More... | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | parse (InputType &&i, const parser_callback_t cb=nullptr, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| deserialize from a compatible input More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | parse (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const parser_callback_t cb=nullptr, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| deserialize from a pair of character iterators More... | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | parse (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const parser_callback_t cb=nullptr, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static bool | accept (InputType &&i, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| check if the input is valid JSON More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static bool | accept (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT bool | accept (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| template<typename InputType , typename SAX > | |
| static bool | sax_parse (InputType &&i, SAX *sax, input_format_t format=input_format_t::json, const bool strict=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| generate SAX events More... | |
| template<class IteratorType , class SAX > | |
| static bool | sax_parse (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, SAX *sax, input_format_t format=input_format_t::json, const bool strict=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
| template<typename SAX > | |
| static bool | sax_parse (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, SAX *sax, input_format_t format=input_format_t::json, const bool strict=true, const bool ignore_comments=false) |
binary serialization/deserialization support | |
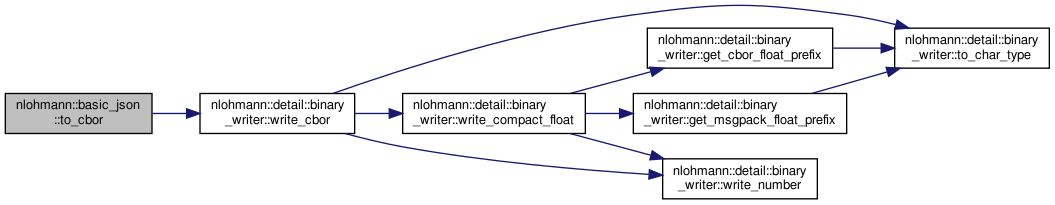
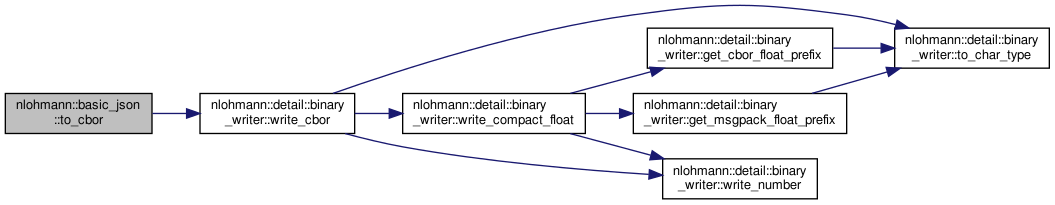
| static std::vector< std::uint8_t > | to_cbor (const basic_json &j) |
| create a CBOR serialization of a given JSON value More... | |
| static void | to_cbor (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< std::uint8_t > o) |
| static void | to_cbor (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< char > o) |
| static std::vector< std::uint8_t > | to_msgpack (const basic_json &j) |
| create a MessagePack serialization of a given JSON value More... | |
| static void | to_msgpack (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< std::uint8_t > o) |
| static void | to_msgpack (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< char > o) |
| static std::vector< std::uint8_t > | to_ubjson (const basic_json &j, const bool use_size=false, const bool use_type=false) |
| create a UBJSON serialization of a given JSON value More... | |
| static void | to_ubjson (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< std::uint8_t > o, const bool use_size=false, const bool use_type=false) |
| static void | to_ubjson (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< char > o, const bool use_size=false, const bool use_type=false) |
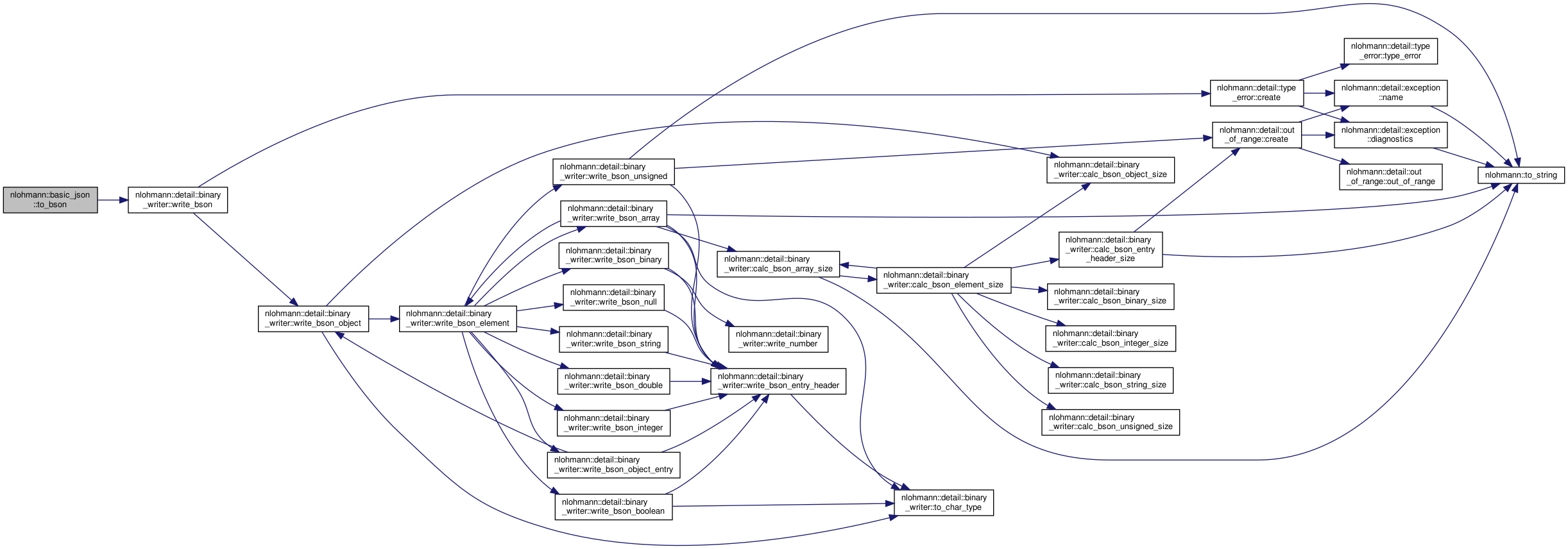
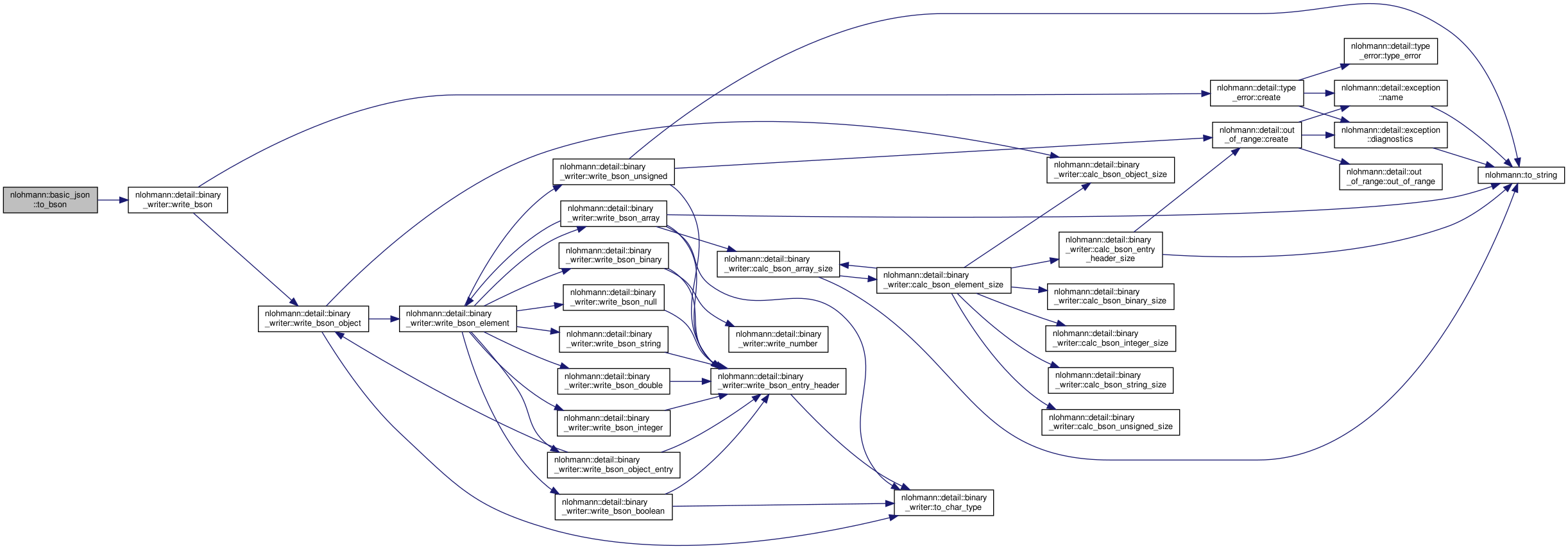
| static std::vector< std::uint8_t > | to_bson (const basic_json &j) |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and returns a vector containing the corresponding BSON-representation. More... | |
| static void | to_bson (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< std::uint8_t > o) |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and forwards the corresponding BSON-representation to the given output_adapter o. More... | |
| static void | to_bson (const basic_json &j, detail::output_adapter< char > o) |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and forwards the corresponding BSON-representation to the given output_adapter o. More... | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_cbor (InputType &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const cbor_tag_handler_t tag_handler=cbor_tag_handler_t::error) |
| create a JSON value from an input in CBOR format More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_cbor (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const cbor_tag_handler_t tag_handler=cbor_tag_handler_t::error) |
| create a JSON value from an input in CBOR format More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_cbor (const T *ptr, std::size_t len, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const cbor_tag_handler_t tag_handler=cbor_tag_handler_t::error) |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_cbor (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true, const cbor_tag_handler_t tag_handler=cbor_tag_handler_t::error) |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_msgpack (InputType &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| create a JSON value from an input in MessagePack format More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_msgpack (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| create a JSON value from an input in MessagePack format More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_msgpack (const T *ptr, std::size_t len, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_msgpack (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_ubjson (InputType &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| create a JSON value from an input in UBJSON format More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_ubjson (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| create a JSON value from an input in UBJSON format More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_ubjson (const T *ptr, std::size_t len, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_ubjson (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_bson (InputType &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| Create a JSON value from an input in BSON format. More... | |
| template<typename IteratorType > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_bson (IteratorType first, IteratorType last, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| Create a JSON value from an input in BSON format. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_bson (const T *ptr, std::size_t len, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | from_bson (detail::span_input_adapter &&i, const bool strict=true, const bool allow_exceptions=true) |
JSON Pointer functions | |
| reference | operator[] (const json_pointer &ptr) |
| access specified element via JSON Pointer More... | |
| const_reference | operator[] (const json_pointer &ptr) const |
| access specified element via JSON Pointer More... | |
| reference | at (const json_pointer &ptr) |
| access specified element via JSON Pointer More... | |
| const_reference | at (const json_pointer &ptr) const |
| access specified element via JSON Pointer More... | |
| basic_json | flatten () const |
| return flattened JSON value More... | |
| basic_json | unflatten () const |
| unflatten a previously flattened JSON value More... | |
JSON Patch functions | |
| static JSON_HEDLEY_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT basic_json | diff (const basic_json &source, const basic_json &target, const std::string &path="") |
| creates a diff as a JSON patch More... | |
| basic_json | patch (const basic_json &json_patch) const |
| applies a JSON patch More... | |
JSON Merge Patch functions | |
| void | merge_patch (const basic_json &apply_patch) |
| applies a JSON Merge Patch More... | |
Detailed Description
a class to store JSON values
- Template Parameters
-
ObjectType type for JSON objects ( std::mapby default; will be used in object_t)ArrayType type for JSON arrays ( std::vectorby default; will be used in array_t)StringType type for JSON strings and object keys ( std::stringby default; will be used in string_t)BooleanType type for JSON booleans ( boolby default; will be used in boolean_t)NumberIntegerType type for JSON integer numbers ( int64_tby default; will be used in number_integer_t)NumberUnsignedType type for JSON unsigned integer numbers ( uint64_tNumberFloatType type for JSON floating-point numbers ( doubleby default; will be used in number_float_t)BinaryType type for packed binary data for compatibility with binary serialization formats ( std::vector<std::uint8_t>by default; will be used in binary_t)AllocatorType type of the allocator to use ( std::allocatorby default)JSONSerializer the serializer to resolve internal calls to to_json()andfrom_json()(adl_serializer by default)
@requirement The class satisfies the following concept requirements:
- Basic
- DefaultConstructible: JSON values can be default constructed. The result will be a JSON null value.
- MoveConstructible: A JSON value can be constructed from an rvalue argument.
- CopyConstructible: A JSON value can be copy-constructed from an lvalue expression.
- MoveAssignable: A JSON value van be assigned from an rvalue argument.
- CopyAssignable: A JSON value can be copy-assigned from an lvalue expression.
- Destructible: JSON values can be destructed.
- Layout
- StandardLayoutType: JSON values have standard layout: All non-static data members are private and standard layout types, the class has no virtual functions or (virtual) base classes.
- Library-wide
- EqualityComparable: JSON values can be compared with
==, see operator==(const_reference,const_reference). - LessThanComparable: JSON values can be compared with
<, see operator<(const_reference,const_reference). - Swappable: Any JSON lvalue or rvalue of can be swapped with any lvalue or rvalue of other compatible types, using unqualified function call swap().
- NullablePointer: JSON values can be compared against
std::nullptr_tobjects which are used to model thenullvalue.
- EqualityComparable: JSON values can be compared with
- Container
- Container: JSON values can be used like STL containers and provide iterator access.
- ReversibleContainer; JSON values can be used like STL containers and provide reverse iterator access.
- Invariant
- The member variables m_value and m_type have the following relationship:
- If
m_type == value_t::object, thenm_value.object != nullptr. - If
m_type == value_t::array, thenm_value.array != nullptr. - If
m_type == value_t::string, thenm_value.string != nullptr. The invariants are checked by member function assert_invariant().
- If
- Note
- ObjectType trick from https://stackoverflow.com/a/9860911
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Member Typedef Documentation
◆ allocator_type
| using nlohmann::basic_json::allocator_type = AllocatorType<basic_json> |
◆ array_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::array_t = ArrayType<basic_json, AllocatorType<basic_json> > |
a type for an array
RFC 8259 describes JSON arrays as follows:
An array is an ordered sequence of zero or more values.
To store objects in C++, a type is defined by the template parameters explained below.
- Template Parameters
-
ArrayType container type to store arrays (e.g., std::vectororstd::list)AllocatorType allocator to use for arrays (e.g., std::allocator)
Default type
With the default values for ArrayType (std::vector) and AllocatorType (std::allocator), the default value for array_t is:
Limits
RFC 8259 specifies:
An implementation may set limits on the maximum depth of nesting.
In this class, the array's limit of nesting is not explicitly constrained. However, a maximum depth of nesting may be introduced by the compiler or runtime environment. A theoretical limit can be queried by calling the max_size function of a JSON array.
Storage
Arrays are stored as pointers in a basic_json type. That is, for any access to array values, a pointer of type array_t* must be dereferenced.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ basic_json_t
|
private |
◆ binary_reader
|
private |
◆ binary_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::binary_t = nlohmann::byte_container_with_subtype<BinaryType> |
a type for a packed binary type
This type is a type designed to carry binary data that appears in various serialized formats, such as CBOR's Major Type 2, MessagePack's bin, and BSON's generic binary subtype. This type is NOT a part of standard JSON and exists solely for compatibility with these binary types. As such, it is simply defined as an ordered sequence of zero or more byte values.
Additionally, as an implementation detail, the subtype of the binary data is carried around as a std::uint8_t, which is compatible with both of the binary data formats that use binary subtyping, (though the specific numbering is incompatible with each other, and it is up to the user to translate between them).
CBOR's RFC 7049 describes this type as:
Major type 2: a byte string. The string's length in bytes is represented following the rules for positive integers (major type 0).
MessagePack's documentation on the bin type family describes this type as:
Bin format family stores an byte array in 2, 3, or 5 bytes of extra bytes in addition to the size of the byte array.
BSON's specifications describe several binary types; however, this type is intended to represent the generic binary type which has the description:
Generic binary subtype - This is the most commonly used binary subtype and should be the 'default' for drivers and tools.
None of these impose any limitations on the internal representation other than the basic unit of storage be some type of array whose parts are decomposable into bytes.
The default representation of this binary format is a std::vector<std::uint8_t>, which is a very common way to represent a byte array in modern C++.
Default type
The default values for BinaryType is std::vector<std::uint8_t>
Storage
Binary Arrays are stored as pointers in a basic_json type. That is, for any access to array values, a pointer of the type binary_t* must be dereferenced.
Notes on subtypes
- CBOR
- Binary values are represented as byte strings. Subtypes are serialized as tagged values.
- MessagePack
- If a subtype is given and the binary array contains exactly 1, 2, 4, 8, or 16 elements, the fixext family (fixext1, fixext2, fixext4, fixext8) is used. For other sizes, the ext family (ext8, ext16, ext32) is used. The subtype is then added as singed 8-bit integer.
- If no subtype is given, the bin family (bin8, bin16, bin32) is used.
- BSON
- If a subtype is given, it is used and added as unsigned 8-bit integer.
- If no subtype is given, the generic binary subtype 0x00 is used.
- Since
- version 3.8.0
◆ binary_writer
|
private |
◆ boolean_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::boolean_t = BooleanType |
a type for a boolean
RFC 8259 implicitly describes a boolean as a type which differentiates the two literals true and false.
To store objects in C++, a type is defined by the template parameter BooleanType which chooses the type to use.
Default type
With the default values for BooleanType (bool), the default value for boolean_t is:
Storage
Boolean values are stored directly inside a basic_json type.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ cbor_tag_handler_t
◆ const_iterator
| using nlohmann::basic_json::const_iterator = iter_impl<const basic_json> |
a const iterator for a basic_json container
◆ const_pointer
| using nlohmann::basic_json::const_pointer = typename std::allocator_traits<allocator_type>::const_pointer |
◆ const_reference
| using nlohmann::basic_json::const_reference = const value_type& |
◆ const_reverse_iterator
| using nlohmann::basic_json::const_reverse_iterator = json_reverse_iterator<typename basic_json::const_iterator> |
a const reverse iterator for a basic_json container
◆ difference_type
| using nlohmann::basic_json::difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t |
◆ error_handler_t
◆ exception
general exception of the basic_json class
This class is an extension of std::exception objects with a member id for exception ids. It is used as the base class for all exceptions thrown by the basic_json class. This class can hence be used as "wildcard" to catch exceptions.
Subclasses:
- parse_error for exceptions indicating a parse error
- invalid_iterator for exceptions indicating errors with iterators
- type_error for exceptions indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
- out_of_range for exceptions indicating access out of the defined range
- other_error for exceptions indicating other library errors
- Note
- To have nothrow-copy-constructible exceptions, we internally use
std::runtime_errorwhich can cope with arbitrary-length error messages. Intermediate strings are built with static functions and then passed to the actual constructor.
@liveexample{The following code shows how arbitrary library exceptions can be caught.,exception}
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ initializer_list_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::initializer_list_t = std::initializer_list<detail::json_ref<basic_json> > |
helper type for initializer lists of basic_json values
◆ input_format_t
◆ internal_iterator
|
private |
◆ invalid_iterator
exception indicating errors with iterators
This exception is thrown if iterators passed to a library function do not match the expected semantics.
Exceptions have ids 2xx.
| name / id | example message | description |
|---|---|---|
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.201 | iterators are not compatible | The iterators passed to constructor basic_json(InputIT first, InputIT last) are not compatible, meaning they do not belong to the same container. Therefore, the range (first, last) is invalid. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.202 | iterator does not fit current value | In an erase or insert function, the passed iterator pos does not belong to the JSON value for which the function was called. It hence does not define a valid position for the deletion/insertion. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.203 | iterators do not fit current value | Either iterator passed to function erase(IteratorType first, IteratorType last) does not belong to the JSON value from which values shall be erased. It hence does not define a valid range to delete values from. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.204 | iterators out of range | When an iterator range for a primitive type (number, boolean, or string) is passed to a constructor or an erase function, this range has to be exactly (begin(), end()), because this is the only way the single stored value is expressed. All other ranges are invalid. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.205 | iterator out of range | When an iterator for a primitive type (number, boolean, or string) is passed to an erase function, the iterator has to be the begin() iterator, because it is the only way to address the stored value. All other iterators are invalid. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.206 | cannot construct with iterators from null | The iterators passed to constructor basic_json(InputIT first, InputIT last) belong to a JSON null value and hence to not define a valid range. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.207 | cannot use key() for non-object iterators | The key() member function can only be used on iterators belonging to a JSON object, because other types do not have a concept of a key. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.208 | cannot use operator[] for object iterators | The operator[] to specify a concrete offset cannot be used on iterators belonging to a JSON object, because JSON objects are unordered. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.209 | cannot use offsets with object iterators | The offset operators (+, -, +=, -=) cannot be used on iterators belonging to a JSON object, because JSON objects are unordered. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.210 | iterators do not fit | The iterator range passed to the insert function are not compatible, meaning they do not belong to the same container. Therefore, the range (first, last) is invalid. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.211 | passed iterators may not belong to container | The iterator range passed to the insert function must not be a subrange of the container to insert to. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.212 | cannot compare iterators of different containers | When two iterators are compared, they must belong to the same container. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.213 | cannot compare order of object iterators | The order of object iterators cannot be compared, because JSON objects are unordered. |
| json.exception.invalid_iterator.214 | cannot get value | Cannot get value for iterator: Either the iterator belongs to a null value or it is an iterator to a primitive type (number, boolean, or string), but the iterator is different to begin(). |
@liveexample{The following code shows how an invalid_iterator exception can be caught.,invalid_iterator}
- See also
- - exception for the base class of the library exceptions
- - parse_error for exceptions indicating a parse error
- - type_error for exceptions indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
- - out_of_range for exceptions indicating access out of the defined range
- - other_error for exceptions indicating other library errors
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ iter_impl
|
private |
◆ iteration_proxy
|
private |
◆ iterator
an iterator for a basic_json container
◆ json_pointer
JSON Pointer, see nlohmann::json_pointer.
◆ json_reverse_iterator
|
private |
◆ json_sax_t
SAX interface type, see nlohmann::json_sax.
◆ json_serializer
| using nlohmann::basic_json::json_serializer = JSONSerializer<T, SFINAE> |
◆ number_float_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::number_float_t = NumberFloatType |
a type for a number (floating-point)
RFC 8259 describes numbers as follows:
The representation of numbers is similar to that used in most programming languages. A number is represented in base 10 using decimal digits. It contains an integer component that may be prefixed with an optional minus sign, which may be followed by a fraction part and/or an exponent part. Leading zeros are not allowed. (...) Numeric values that cannot be represented in the grammar below (such as Infinity and NaN) are not permitted.
This description includes both integer and floating-point numbers. However, C++ allows more precise storage if it is known whether the number is a signed integer, an unsigned integer or a floating-point number. Therefore, three different types, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t and number_float_t are used.
To store floating-point numbers in C++, a type is defined by the template parameter NumberFloatType which chooses the type to use.
Default type
With the default values for NumberFloatType (double), the default value for number_float_t is:
Default behavior
- The restrictions about leading zeros is not enforced in C++. Instead, leading zeros in floating-point literals will be ignored. Internally, the value will be stored as decimal number. For instance, the C++ floating-point literal
01.2will be serialized to1.2. During deserialization, leading zeros yield an error. - Not-a-number (NaN) values will be serialized to
null.
Limits
RFC 8259 states:
This specification allows implementations to set limits on the range and precision of numbers accepted. Since software that implements IEEE 754-2008 binary64 (double precision) numbers is generally available and widely used, good interoperability can be achieved by implementations that expect no more precision or range than these provide, in the sense that implementations will approximate JSON numbers within the expected precision.
This implementation does exactly follow this approach, as it uses double precision floating-point numbers. Note values smaller than -1.79769313486232e+308 and values greater than 1.79769313486232e+308 will be stored as NaN internally and be serialized to null.
Storage
Floating-point number values are stored directly inside a basic_json type.
- See also
- see number_integer_t – type for number values (integer)
- see number_unsigned_t – type for number values (unsigned integer)
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ number_integer_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::number_integer_t = NumberIntegerType |
a type for a number (integer)
RFC 8259 describes numbers as follows:
The representation of numbers is similar to that used in most programming languages. A number is represented in base 10 using decimal digits. It contains an integer component that may be prefixed with an optional minus sign, which may be followed by a fraction part and/or an exponent part. Leading zeros are not allowed. (...) Numeric values that cannot be represented in the grammar below (such as Infinity and NaN) are not permitted.
This description includes both integer and floating-point numbers. However, C++ allows more precise storage if it is known whether the number is a signed integer, an unsigned integer or a floating-point number. Therefore, three different types, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t and number_float_t are used.
To store integer numbers in C++, a type is defined by the template parameter NumberIntegerType which chooses the type to use.
Default type
With the default values for NumberIntegerType (int64_t), the default value for number_integer_t is:
Default behavior
- The restrictions about leading zeros is not enforced in C++. Instead, leading zeros in integer literals lead to an interpretation as octal number. Internally, the value will be stored as decimal number. For instance, the C++ integer literal
010will be serialized to8. During deserialization, leading zeros yield an error. - Not-a-number (NaN) values will be serialized to
null.
Limits
RFC 8259 specifies:
An implementation may set limits on the range and precision of numbers.
When the default type is used, the maximal integer number that can be stored is 9223372036854775807 (INT64_MAX) and the minimal integer number that can be stored is -9223372036854775808 (INT64_MIN). Integer numbers that are out of range will yield over/underflow when used in a constructor. During deserialization, too large or small integer numbers will be automatically be stored as number_unsigned_t or number_float_t.
RFC 8259 further states:
Note that when such software is used, numbers that are integers and are in the range
are interoperable in the sense that implementations will agree exactly on their numeric values.
As this range is a subrange of the exactly supported range [INT64_MIN, INT64_MAX], this class's integer type is interoperable.
Storage
Integer number values are stored directly inside a basic_json type.
- See also
- see number_float_t – type for number values (floating-point)
- see number_unsigned_t – type for number values (unsigned integer)
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ number_unsigned_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::number_unsigned_t = NumberUnsignedType |
a type for a number (unsigned)
RFC 8259 describes numbers as follows:
The representation of numbers is similar to that used in most programming languages. A number is represented in base 10 using decimal digits. It contains an integer component that may be prefixed with an optional minus sign, which may be followed by a fraction part and/or an exponent part. Leading zeros are not allowed. (...) Numeric values that cannot be represented in the grammar below (such as Infinity and NaN) are not permitted.
This description includes both integer and floating-point numbers. However, C++ allows more precise storage if it is known whether the number is a signed integer, an unsigned integer or a floating-point number. Therefore, three different types, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t and number_float_t are used.
To store unsigned integer numbers in C++, a type is defined by the template parameter NumberUnsignedType which chooses the type to use.
Default type
With the default values for NumberUnsignedType (uint64_t), the default value for number_unsigned_t is:
Default behavior
- The restrictions about leading zeros is not enforced in C++. Instead, leading zeros in integer literals lead to an interpretation as octal number. Internally, the value will be stored as decimal number. For instance, the C++ integer literal
010will be serialized to8. During deserialization, leading zeros yield an error. - Not-a-number (NaN) values will be serialized to
null.
Limits
RFC 8259 specifies:
An implementation may set limits on the range and precision of numbers.
When the default type is used, the maximal integer number that can be stored is 18446744073709551615 (UINT64_MAX) and the minimal integer number that can be stored is 0. Integer numbers that are out of range will yield over/underflow when used in a constructor. During deserialization, too large or small integer numbers will be automatically be stored as number_integer_t or number_float_t.
RFC 8259 further states:
Note that when such software is used, numbers that are integers and are in the range
are interoperable in the sense that implementations will agree exactly on their numeric values.
As this range is a subrange (when considered in conjunction with the number_integer_t type) of the exactly supported range [0, UINT64_MAX], this class's integer type is interoperable.
Storage
Integer number values are stored directly inside a basic_json type.
- See also
- see number_float_t – type for number values (floating-point)
- see number_integer_t – type for number values (integer)
- Since
- version 2.0.0
◆ object_comparator_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::object_comparator_t = std::less<StringType> |
◆ object_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::object_t = ObjectType<StringType, basic_json, object_comparator_t, AllocatorType<std::pair<const StringType, basic_json> >> |
a type for an object
RFC 8259 describes JSON objects as follows:
An object is an unordered collection of zero or more name/value pairs, where a name is a string and a value is a string, number, boolean, null, object, or array.
To store objects in C++, a type is defined by the template parameters described below.
- Template Parameters
-
ObjectType the container to store objects (e.g., std::maporstd::unordered_map)StringType the type of the keys or names (e.g., std::string). The comparison functionstd::less<StringType>is used to order elements inside the container.AllocatorType the allocator to use for objects (e.g., std::allocator)
Default type
With the default values for ObjectType (std::map), StringType (std::string), and AllocatorType (std::allocator), the default value for object_t is:
Behavior
The choice of object_t influences the behavior of the JSON class. With the default type, objects have the following behavior:
- When all names are unique, objects will be interoperable in the sense that all software implementations receiving that object will agree on the name-value mappings.
- When the names within an object are not unique, it is unspecified which one of the values for a given key will be chosen. For instance,
{"key": 2, "key": 1}could be equal to either{"key": 1}or{"key": 2}. - Internally, name/value pairs are stored in lexicographical order of the names. Objects will also be serialized (see dump) in this order. For instance,
{"b": 1, "a": 2}and{"a": 2, "b": 1}will be stored and serialized as{"a": 2, "b": 1}. - When comparing objects, the order of the name/value pairs is irrelevant. This makes objects interoperable in the sense that they will not be affected by these differences. For instance,
{"b": 1, "a": 2}and{"a": 2, "b": 1}will be treated as equal.
Limits
RFC 8259 specifies:
An implementation may set limits on the maximum depth of nesting.
In this class, the object's limit of nesting is not explicitly constrained. However, a maximum depth of nesting may be introduced by the compiler or runtime environment. A theoretical limit can be queried by calling the max_size function of a JSON object.
Storage
Objects are stored as pointers in a basic_json type. That is, for any access to object values, a pointer of type object_t* must be dereferenced.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
- Note
- The order name/value pairs are added to the object is not preserved by the library. Therefore, iterating an object may return name/value pairs in a different order than they were originally stored. In fact, keys will be traversed in alphabetical order as
std::mapwithstd::lessis used by default. Please note this behavior conforms to RFC 8259, because any order implements the specified "unordered" nature of JSON objects.
◆ other_error
exception indicating other library errors
This exception is thrown in case of errors that cannot be classified with the other exception types.
Exceptions have ids 5xx.
| name / id | example message | description |
|---|---|---|
| json.exception.other_error.501 | unsuccessful: {"op":"test","path":"/baz", "value":"bar"} | A JSON Patch operation 'test' failed. The unsuccessful operation is also printed. |
- See also
- - exception for the base class of the library exceptions
- - parse_error for exceptions indicating a parse error
- - invalid_iterator for exceptions indicating errors with iterators
- - type_error for exceptions indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
- - out_of_range for exceptions indicating access out of the defined range
@liveexample{The following code shows how an other_error exception can be caught.,other_error}
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ out_of_range
exception indicating access out of the defined range
This exception is thrown in case a library function is called on an input parameter that exceeds the expected range, for instance in case of array indices or nonexisting object keys.
Exceptions have ids 4xx.
| name / id | example message | description |
|---|---|---|
| json.exception.out_of_range.401 | array index 3 is out of range | The provided array index i is larger than size-1. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.402 | array index '-' (3) is out of range | The special array index - in a JSON Pointer never describes a valid element of the array, but the index past the end. That is, it can only be used to add elements at this position, but not to read it. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.403 | key 'foo' not found | The provided key was not found in the JSON object. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.404 | unresolved reference token 'foo' | A reference token in a JSON Pointer could not be resolved. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.405 | JSON pointer has no parent | The JSON Patch operations 'remove' and 'add' can not be applied to the root element of the JSON value. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.406 | number overflow parsing '10E1000' | A parsed number could not be stored as without changing it to NaN or INF. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.407 | number overflow serializing '9223372036854775808' | UBJSON and BSON only support integer numbers up to 9223372036854775807. (until version 3.8.0) |
| json.exception.out_of_range.408 | excessive array size: 8658170730974374167 | The size (following #) of an UBJSON array or object exceeds the maximal capacity. |
| json.exception.out_of_range.409 | BSON key cannot contain code point U+0000 (at byte 2) | Key identifiers to be serialized to BSON cannot contain code point U+0000, since the key is stored as zero-terminated c-string |
@liveexample{The following code shows how an out_of_range exception can be caught.,out_of_range}
- See also
- - exception for the base class of the library exceptions
- - parse_error for exceptions indicating a parse error
- - invalid_iterator for exceptions indicating errors with iterators
- - type_error for exceptions indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
- - other_error for exceptions indicating other library errors
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ output_adapter_t
|
private |
◆ parse_error
exception indicating a parse error
This exception is thrown by the library when a parse error occurs. Parse errors can occur during the deserialization of JSON text, CBOR, MessagePack, as well as when using JSON Patch.
Member byte holds the byte index of the last read character in the input file.
Exceptions have ids 1xx.
| name / id | example message | description |
|---|---|---|
| json.exception.parse_error.101 | parse error at 2: unexpected end of input; expected string literal | This error indicates a syntax error while deserializing a JSON text. The error message describes that an unexpected token (character) was encountered, and the member byte indicates the error position. |
| json.exception.parse_error.102 | parse error at 14: missing or wrong low surrogate | JSON uses the \uxxxx format to describe Unicode characters. Code points above above 0xFFFF are split into two \uxxxx entries ("surrogate pairs"). This error indicates that the surrogate pair is incomplete or contains an invalid code point. |
| json.exception.parse_error.103 | parse error: code points above 0x10FFFF are invalid | Unicode supports code points up to 0x10FFFF. Code points above 0x10FFFF are invalid. |
| json.exception.parse_error.104 | parse error: JSON patch must be an array of objects | RFC 6902 requires a JSON Patch document to be a JSON document that represents an array of objects. |
| json.exception.parse_error.105 | parse error: operation must have string member 'op' | An operation of a JSON Patch document must contain exactly one "op" member, whose value indicates the operation to perform. Its value must be one of "add", "remove", "replace", "move", "copy", or "test"; other values are errors. |
| json.exception.parse_error.106 | parse error: array index '01' must not begin with '0' | An array index in a JSON Pointer (RFC 6901) may be 0 or any number without a leading 0. |
| json.exception.parse_error.107 | parse error: JSON pointer must be empty or begin with '/' - was: 'foo' | A JSON Pointer must be a Unicode string containing a sequence of zero or more reference tokens, each prefixed by a / character. |
| json.exception.parse_error.108 | parse error: escape character '~' must be followed with '0' or '1' | In a JSON Pointer, only ~0 and ~1 are valid escape sequences. |
| json.exception.parse_error.109 | parse error: array index 'one' is not a number | A JSON Pointer array index must be a number. |
| json.exception.parse_error.110 | parse error at 1: cannot read 2 bytes from vector | When parsing CBOR or MessagePack, the byte vector ends before the complete value has been read. |
| json.exception.parse_error.112 | parse error at 1: error reading CBOR; last byte: 0xF8 | Not all types of CBOR or MessagePack are supported. This exception occurs if an unsupported byte was read. |
| json.exception.parse_error.113 | parse error at 2: expected a CBOR string; last byte: 0x98 | While parsing a map key, a value that is not a string has been read. |
| json.exception.parse_error.114 | parse error: Unsupported BSON record type 0x0F | The parsing of the corresponding BSON record type is not implemented (yet). |
| json.exception.parse_error.115 | parse error at byte 5: syntax error while parsing UBJSON high-precision number: invalid number text: 1A | A UBJSON high-precision number could not be parsed. |
- Note
- For an input with n bytes, 1 is the index of the first character and n+1 is the index of the terminating null byte or the end of file. This also holds true when reading a byte vector (CBOR or MessagePack).
@liveexample{The following code shows how a parse_error exception can be caught.,parse_error}
- See also
- - exception for the base class of the library exceptions
- - invalid_iterator for exceptions indicating errors with iterators
- - type_error for exceptions indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
- - out_of_range for exceptions indicating access out of the defined range
- - other_error for exceptions indicating other library errors
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ parse_event_t
parser event types
The parser callback distinguishes the following events:
object_start: the parser read{and started to process a JSON objectkey: the parser read a key of a value in an objectobject_end: the parser read}and finished processing a JSON objectarray_start: the parser read[and started to process a JSON arrayarray_end: the parser read]and finished processing a JSON arrayvalue: the parser finished reading a JSON value

- See also
- see parser_callback_t for more information and examples
◆ parser_callback_t
per-element parser callback type
With a parser callback function, the result of parsing a JSON text can be influenced. When passed to parse, it is called on certain events (passed as parse_event_t via parameter event) with a set recursion depth depth and context JSON value parsed. The return value of the callback function is a boolean indicating whether the element that emitted the callback shall be kept or not.
We distinguish six scenarios (determined by the event type) in which the callback function can be called. The following table describes the values of the parameters depth, event, and parsed.
| parameter event | description | parameter depth | parameter parsed |
|---|---|---|---|
| parse_event_t::object_start | the parser read { and started to process a JSON object | depth of the parent of the JSON object | a JSON value with type discarded |
| parse_event_t::key | the parser read a key of a value in an object | depth of the currently parsed JSON object | a JSON string containing the key |
| parse_event_t::object_end | the parser read } and finished processing a JSON object | depth of the parent of the JSON object | the parsed JSON object |
| parse_event_t::array_start | the parser read [ and started to process a JSON array | depth of the parent of the JSON array | a JSON value with type discarded |
| parse_event_t::array_end | the parser read ] and finished processing a JSON array | depth of the parent of the JSON array | the parsed JSON array |
| parse_event_t::value | the parser finished reading a JSON value | depth of the value | the parsed JSON value |

Discarding a value (i.e., returning false) has different effects depending on the context in which function was called:
- Discarded values in structured types are skipped. That is, the parser will behave as if the discarded value was never read.
- In case a value outside a structured type is skipped, it is replaced with
null. This case happens if the top-level element is skipped.
- Parameters
-
[in] depth the depth of the recursion during parsing [in] event an event of type parse_event_t indicating the context in the callback function has been called [in,out] parsed the current intermediate parse result; note that writing to this value has no effect for parse_event_t::key events
- Returns
- Whether the JSON value which called the function during parsing should be kept (
true) or not (false). In the latter case, it is either skipped completely or replaced by an empty discarded object.
- See also
- see parse for examples
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ pointer
| using nlohmann::basic_json::pointer = typename std::allocator_traits<allocator_type>::pointer |
◆ primitive_iterator_t
◆ reference
◆ reverse_iterator
| using nlohmann::basic_json::reverse_iterator = json_reverse_iterator<typename basic_json::iterator> |
a reverse iterator for a basic_json container
◆ size_type
| using nlohmann::basic_json::size_type = std::size_t |
◆ string_t
| using nlohmann::basic_json::string_t = StringType |
a type for a string
RFC 8259 describes JSON strings as follows:
A string is a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters.
To store objects in C++, a type is defined by the template parameter described below. Unicode values are split by the JSON class into byte-sized characters during deserialization.
- Template Parameters
-
StringType the container to store strings (e.g., std::string). Note this container is used for keys/names in objects, see object_t.
Default type
With the default values for StringType (std::string), the default value for string_t is:
Encoding
Strings are stored in UTF-8 encoding. Therefore, functions like std::string::size() or std::string::length() return the number of bytes in the string rather than the number of characters or glyphs.
String comparison
RFC 8259 states:
Software implementations are typically required to test names of object members for equality. Implementations that transform the textual representation into sequences of Unicode code units and then perform the comparison numerically, code unit by code unit, are interoperable in the sense that implementations will agree in all cases on equality or inequality of two strings. For example, implementations that compare strings with escaped characters unconverted may incorrectly find that
"a\\b"and"a\u005Cb"are not equal.
This implementation is interoperable as it does compare strings code unit by code unit.
Storage
String values are stored as pointers in a basic_json type. That is, for any access to string values, a pointer of type string_t* must be dereferenced.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ type_error
exception indicating executing a member function with a wrong type
This exception is thrown in case of a type error; that is, a library function is executed on a JSON value whose type does not match the expected semantics.
Exceptions have ids 3xx.
| name / id | example message | description |
|---|---|---|
| json.exception.type_error.301 | cannot create object from initializer list | To create an object from an initializer list, the initializer list must consist only of a list of pairs whose first element is a string. When this constraint is violated, an array is created instead. |
| json.exception.type_error.302 | type must be object, but is array | During implicit or explicit value conversion, the JSON type must be compatible to the target type. For instance, a JSON string can only be converted into string types, but not into numbers or boolean types. |
| json.exception.type_error.303 | incompatible ReferenceType for get_ref, actual type is object | To retrieve a reference to a value stored in a basic_json object with get_ref, the type of the reference must match the value type. For instance, for a JSON array, the ReferenceType must be array_t &. |
| json.exception.type_error.304 | cannot use at() with string | The at() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.305 | cannot use operator[] with string | The operator[] member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.306 | cannot use value() with string | The value() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.307 | cannot use erase() with string | The erase() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.308 | cannot use push_back() with string | The push_back() and operator+= member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.309 | cannot use insert() with | The insert() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.310 | cannot use swap() with number | The swap() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.311 | cannot use emplace_back() with string | The emplace_back() member function can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.312 | cannot use update() with string | The update() member functions can only be executed for certain JSON types. |
| json.exception.type_error.313 | invalid value to unflatten | The unflatten function converts an object whose keys are JSON Pointers back into an arbitrary nested JSON value. The JSON Pointers must not overlap, because then the resulting value would not be well defined. |
| json.exception.type_error.314 | only objects can be unflattened | The unflatten function only works for an object whose keys are JSON Pointers. |
| json.exception.type_error.315 | values in object must be primitive | The unflatten function only works for an object whose keys are JSON Pointers and whose values are primitive. |
| json.exception.type_error.316 | invalid UTF-8 byte at index 10: 0x7E | The dump function only works with UTF-8 encoded strings; that is, if you assign a std::string to a JSON value, make sure it is UTF-8 encoded. |
| json.exception.type_error.317 | JSON value cannot be serialized to requested format | The dynamic type of the object cannot be represented in the requested serialization format (e.g. a raw true or null JSON object cannot be serialized to BSON) |
@liveexample{The following code shows how a type_error exception can be caught.,type_error}
- See also
- - exception for the base class of the library exceptions
- - parse_error for exceptions indicating a parse error
- - invalid_iterator for exceptions indicating errors with iterators
- - out_of_range for exceptions indicating access out of the defined range
- - other_error for exceptions indicating other library errors
- Since
- version 3.0.0
◆ value_t
◆ value_type
the type of elements in a basic_json container
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ basic_json() [1/10]
|
inline |
create an empty value with a given type
Create an empty JSON value with a given type. The value will be default initialized with an empty value which depends on the type:
| Value type | initial value |
|---|---|
| null | null |
| boolean | false |
| string | "" |
| number | 0 |
| object | {} |
| array | [] |
| binary | empty array |
- Parameters
-
[in] v the type of the value to create
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows the constructor for different value_t values,basic_json__value_t}
- See also
- see clear() – restores the postcondition of this constructor
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 18840 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant().
Referenced by basic_json(), binary(), from_bson(), from_cbor(), from_msgpack(), from_ubjson(), json_value(), and push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [2/10]
|
inlinenoexcept |
create a null object
Create a null JSON value. It either takes a null pointer as parameter (explicitly creating null) or no parameter (implicitly creating null). The passed null pointer itself is not read – it is only used to choose the right constructor.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this constructor never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code shows the constructor with and without a null pointer parameter.,basic_json__nullptr_t}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 18864 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [3/10]
|
inlinenoexcept |
create a JSON value
This is a "catch all" constructor for all compatible JSON types; that is, types for which a to_json() method exists. The constructor forwards the parameter val to that method (to json_serializer<U>::to_json method with U = uncvref_t<CompatibleType>, to be exact).
Template type CompatibleType includes, but is not limited to, the following types:
- arrays: array_t and all kinds of compatible containers such as
std::vector,std::deque,std::list,std::forward_list,std::array,std::valarray,std::set,std::unordered_set,std::multiset, andstd::unordered_multisetwith avalue_typefrom which a basic_json value can be constructed. - objects: object_t and all kinds of compatible associative containers such as
std::map,std::unordered_map,std::multimap, andstd::unordered_multimapwith akey_typecompatible to string_t and avalue_typefrom which a basic_json value can be constructed. - strings: string_t, string literals, and all compatible string containers can be used.
- numbers: number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t, number_float_t, and all convertible number types such as
int,size_t,int64_t,floatordoublecan be used. - boolean: boolean_t /
boolcan be used. - binary: binary_t /
std::vector<std::uint8_t>may be used, unfortunately because string literals cannot be distinguished from binary character arrays by the C++ type system, all types compatible withconst char*will be directed to the string constructor instead. This is both for backwards compatibility, and due to the fact that a binary type is not a standard JSON type.
See the examples below.
- Template Parameters
-
CompatibleType a type such that: - CompatibleType is not derived from
std::istream, - CompatibleType is not basic_json (to avoid hijacking copy/move constructors),
- CompatibleType is not a different basic_json type (i.e. with different template arguments)
- CompatibleType is not a basic_json nested type (e.g., json_pointer, iterator, etc ...)
json_serializer<U>has ato_json(basic_json_t&, CompatibleType&&)method
U = uncvref_t<CompatibleType> - CompatibleType is not derived from
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to be forwarded to the respective constructor
@complexity Usually linear in the size of the passed val, also depending on the implementation of the called to_json() method.
@exceptionsafety Depends on the called constructor. For types directly supported by the library (i.e., all types for which no to_json() function was provided), strong guarantee holds: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows the constructor with several compatible types.,basic_json__CompatibleType}
- Since
- version 2.1.0
Definition at line 18936 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), set_parents(), and nlohmann::detail::to_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [4/10]
|
inline |
create a JSON value from an existing one
This is a constructor for existing basic_json types. It does not hijack copy/move constructors, since the parameter has different template arguments than the current ones.
The constructor tries to convert the internal m_value of the parameter.
- Template Parameters
-
BasicJsonType a type such that: - BasicJsonType is a basic_json type.
- BasicJsonType has different template arguments than basic_json_t.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the basic_json value to be converted.
@complexity Usually linear in the size of the passed val, also depending on the implementation of the called to_json() method.
@exceptionsafety Depends on the called constructor. For types directly supported by the library (i.e., all types for which no to_json() function was provided), strong guarantee holds: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
- Since
- version 3.2.0
Definition at line 18974 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, JSON_ASSERT, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, set_parents(), nlohmann::detail::string, and nlohmann::detail::to_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [5/10]
|
inline |
create a container (array or object) from an initializer list
Creates a JSON value of type array or object from the passed initializer list init. In case type_deduction is true (default), the type of the JSON value to be created is deducted from the initializer list init according to the following rules:
- If the list is empty, an empty JSON object value
{}is created. - If the list consists of pairs whose first element is a string, a JSON object value is created where the first elements of the pairs are treated as keys and the second elements are as values.
- In all other cases, an array is created.
The rules aim to create the best fit between a C++ initializer list and JSON values. The rationale is as follows:
- The empty initializer list is written as
{}which is exactly an empty JSON object. - C++ has no way of describing mapped types other than to list a list of pairs. As JSON requires that keys must be of type string, rule 2 is the weakest constraint one can pose on initializer lists to interpret them as an object.
- In all other cases, the initializer list could not be interpreted as JSON object type, so interpreting it as JSON array type is safe.
With the rules described above, the following JSON values cannot be expressed by an initializer list:
- the empty array (
[]): use array(initializer_list_t) with an empty initializer list in this case - arrays whose elements satisfy rule 2: use array(initializer_list_t) with the same initializer list in this case
- Note
- When used without parentheses around an empty initializer list, basic_json() is called instead of this function, yielding the JSON null value.
- Parameters
-
[in] init initializer list with JSON values [in] type_deduction internal parameter; when set to true, the type of the JSON value is deducted from the initializer list init; when set tofalse, the type provided via manual_type is forced. This mode is used by the functions array(initializer_list_t) and object(initializer_list_t).[in] manual_type internal parameter; when type_deduction is set to false, the created JSON value will use the provided type (only value_t::array and value_t::object are valid); when type_deduction is set totrue, this parameter has no effect
- Exceptions
-
type_error.301 if type_deduction is false, manual_type isvalue_t::object, but init contains an element which is not a pair whose first element is a string. In this case, the constructor could not create an object. If type_deduction would have betrue, an array would have been created. See object(initializer_list_t) for an example.
@complexity Linear in the size of the initializer list init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The example below shows how JSON values are created from initializer lists.,basic_json__list_init_t}
- See also
- see array(initializer_list_t) – create a JSON array value from an initializer list
- see object(initializer_list_t) – create a JSON object value from an initializer list
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19098 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), board::element, init(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::json_ref< BasicJsonType >::moved_or_copied(), nlohmann::detail::object, and set_parents().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [6/10]
|
inline |
construct an array with count copies of given value
Constructs a JSON array value by creating cnt copies of a passed value. In case cnt is 0, an empty array is created.
- Parameters
-
[in] cnt the number of JSON copies of val to create [in] val the JSON value to copy
@complexity Linear in cnt.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows examples for the basic_json(size_type\, const basic_json&) constructor.,basic_json__size_type_basic_json}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19353 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), m_value, and set_parents().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [7/10]
|
inline |
construct a JSON container given an iterator range
Constructs the JSON value with the contents of the range [first, last). The semantics depends on the different types a JSON value can have:
- In case of a null type, invalid_iterator.206 is thrown.
- In case of other primitive types (number, boolean, or string), first must be
begin()and last must beend(). In this case, the value is copied. Otherwise, invalid_iterator.204 is thrown. - In case of structured types (array, object), the constructor behaves as similar versions for
std::vectororstd::map; that is, a JSON array or object is constructed from the values in the range.
- Template Parameters
-
InputIT an input iterator type (iterator or const_iterator)
- Parameters
-
[in] first begin of the range to copy from (included) [in] last end of the range to copy from (excluded)
- Precondition
- Iterators first and last must be initialized. This precondition is enforced with an assertion (see warning). If assertions are switched off, a violation of this precondition yields undefined behavior.
-
Range
[first, last)is valid. Usually, this precondition cannot be checked efficiently. Only certain edge cases are detected; see the description of the exceptions below. A violation of this precondition yields undefined behavior.
- Warning
- A precondition is enforced with a runtime assertion that will result in calling
std::abortif this precondition is not met. Assertions can be disabled by definingNDEBUGat compile time. See https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/assert for more information.
- Exceptions
-
invalid_iterator.201 if iterators first and last are not compatible (i.e., do not belong to the same JSON value). In this case, the range [first, last)is undefined.invalid_iterator.204 if iterators first and last belong to a primitive type (number, boolean, or string), but first does not point to the first element any more. In this case, the range [first, last)is undefined. See example code below.invalid_iterator.206 if iterators first and last belong to a null value. In this case, the range [first, last)is undefined.
@complexity Linear in distance between first and last.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The example below shows several ways to create JSON values by specifying a subrange with iterators.,basic_json__InputIt_InputIt}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19419 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, JSON_ASSERT, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, set_parents(), and nlohmann::detail::string.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [8/10]
|
inline |
◆ basic_json() [9/10]
|
inline |
copy constructor
Creates a copy of a given JSON value.
- Parameters
-
[in] other the JSON value to copy
- Postcondition
*this == other
@complexity Linear in the size of other.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is linear.
- As postcondition, it holds:
other == basic_json(other).
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for the copy constructor.,basic_json__basic_json}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19556 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, set_parents(), and nlohmann::detail::string.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ basic_json() [10/10]
|
inlinenoexcept |
move constructor
Move constructor. Constructs a JSON value with the contents of the given value other using move semantics. It "steals" the resources from other and leaves it as JSON null value.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other value to move to this object
- Postcondition
*thishas the same value as other before the call.- other is a JSON null value.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this constructor never throws exceptions.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the MoveConstructible requirements.
@liveexample{The code below shows the move constructor explicitly called via std::move.,basic_json__moveconstructor}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19648 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::null, and set_parents().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ ~basic_json()
|
inlinenoexcept |
destructor
Destroys the JSON value and frees all allocated memory.
@complexity Linear.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is linear.
- All stored elements are destroyed and all memory is freed.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19720 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:Member Function Documentation
◆ accept() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
◆ accept() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
check if the input is valid JSON
Unlike the parse(InputType&&, const parser_callback_t,const bool) function, this function neither throws an exception in case of invalid JSON input (i.e., a parse error) nor creates diagnostic information.
- Template Parameters
-
InputType A compatible input, for instance - an std::istream object
- a FILE pointer
- a C-style array of characters
- a pointer to a null-terminated string of single byte characters
- an object obj for which begin(obj) and end(obj) produces a valid pair of iterators.
- Parameters
-
[in] i input to read from [in] ignore_comments whether comments should be ignored and treated like whitespace (true) or yield a parse error (true); (optional, false by default)
- Returns
- Whether the input read from i is valid JSON.
@complexity Linear in the length of the input. The parser is a predictive LL(1) parser.
- Note
- A UTF-8 byte order mark is silently ignored.
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the accept() function reading from a string.,accept__string}
Definition at line 24339 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), and parser().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ accept() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24346 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), and parser().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ array()
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create an array from an initializer list
Creates a JSON array value from a given initializer list. That is, given a list of values a, b, c, creates the JSON value [a, b, c]. If the initializer list is empty, the empty array [] is created.
- Note
- This function is only needed to express two edge cases that cannot be realized with the initializer list constructor (basic_json(initializer_list_t, bool, value_t)). These cases are:
- creating an array whose elements are all pairs whose first element is a string – in this case, the initializer list constructor would create an object, taking the first elements as keys
- creating an empty array – passing the empty initializer list to the initializer list constructor yields an empty object
- Parameters
-
[in] init initializer list with JSON values to create an array from (optional)
- Returns
- JSON array value
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for the array function.,array}
- See also
- see basic_json(initializer_list_t, bool, value_t) – create a JSON value from an initializer list
- see object(initializer_list_t) – create a JSON object value from an initializer list
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ assert_invariant()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
checks the class invariants
This function asserts the class invariants. It needs to be called at the end of every constructor to make sure that created objects respect the invariant. Furthermore, it has to be called each time the type of a JSON value is changed, because the invariant expresses a relationship between m_type and m_value.
Furthermore, the parent relation is checked for arrays and objects: If check_parents true and the value is an array or object, then the container's elements must have the current value as parent.
- Parameters
-
[in] check_parents whether the parent relation should be checked. The value is true by default and should only be set to false during destruction of objects when the invariant does not need to hold.
Definition at line 18634 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, begin(), nlohmann::detail::binary, end(), is_structured(), JSON_ASSERT, JSON_CATCH, JSON_TRY, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by basic_json(), emplace(), emplace_back(), erase(), operator=(), operator[](), push_back(), swap(), update(), and ~basic_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ at() [1/6]
|
inline |
access specified element via JSON Pointer
Returns a reference to the element at with specified JSON pointer ptr, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr JSON pointer to the desired element
- Returns
- reference to the element pointed to by ptr
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.106 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr begins with '0'. See example below. parse_error.109 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr is not a number. See example below. out_of_range.401 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr is out of range. See example below. out_of_range.402 if the array index '-' is used in the passed JSON pointer ptr. As atprovides checked access (and no elements are implicitly inserted), the index '-' is always invalid. See example below.out_of_range.403 if the JSON pointer describes a key of an object which cannot be found. See example below. out_of_range.404 if the JSON pointer ptr can not be resolved. See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 2.0.0
@liveexample{The behavior is shown in the example.,at_json_pointer}
◆ at() [2/6]
|
inline |
access specified element via JSON Pointer
Returns a const reference to the element at with specified JSON pointer ptr, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr JSON pointer to the desired element
- Returns
- reference to the element pointed to by ptr
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.106 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr begins with '0'. See example below. parse_error.109 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr is not a number. See example below. out_of_range.401 if an array index in the passed JSON pointer ptr is out of range. See example below. out_of_range.402 if the array index '-' is used in the passed JSON pointer ptr. As atprovides checked access (and no elements are implicitly inserted), the index '-' is always invalid. See example below.out_of_range.403 if the JSON pointer describes a key of an object which cannot be found. See example below. out_of_range.404 if the JSON pointer ptr can not be resolved. See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 2.0.0
@liveexample{The behavior is shown in the example.,at_json_pointer_const}
◆ at() [3/6]
|
inline |
access specified object element with bounds checking
Returns a reference to the element at with specified key key, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- reference to the element at key key
- Exceptions
-
type_error.304 if the JSON value is not an object; in this case, calling atwith a key makes no sense. See example below.out_of_range.403 if the key key is is not stored in the object; that is, find(key) == end(). See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
- See also
- see operator[](const typename object_t::key_type&) for unchecked access by reference
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.0.0
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read and written using at(). It also demonstrates the different exceptions that can be thrown.,at__object_t_key_type}
Definition at line 20950 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), is_object(), JSON_CATCH, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, m_value, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ at() [4/6]
|
inline |
access specified object element with bounds checking
Returns a const reference to the element at with specified key key, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- const reference to the element at key key
- Exceptions
-
type_error.304 if the JSON value is not an object; in this case, calling atwith a key makes no sense. See example below.out_of_range.403 if the key key is is not stored in the object; that is, find(key) == end(). See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
- See also
- see operator[](const typename object_t::key_type&) for unchecked access by reference
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.0.0
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read using at(). It also demonstrates the different exceptions that can be thrown., at__object_t_key_type_const}
Definition at line 21001 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), is_object(), JSON_CATCH, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ at() [5/6]
access specified array element with bounds checking
Returns a reference to the element at specified location idx, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] idx index of the element to access
- Returns
- reference to the element at index idx
- Exceptions
-
type_error.304 if the JSON value is not an array; in this case, calling atwith an index makes no sense. See example below.out_of_range.401 if the index idx is out of range of the array; that is, idx >= size(). See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
@liveexample{The example below shows how array elements can be read and written using at(). It also demonstrates the different exceptions that can be thrown.,at__size_type}
Definition at line 20852 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), is_array(), JSON_CATCH, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, m_value, set_parent(), nlohmann::to_string(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ at() [6/6]
|
inline |
access specified array element with bounds checking
Returns a const reference to the element at specified location idx, with bounds checking.
- Parameters
-
[in] idx index of the element to access
- Returns
- const reference to the element at index idx
- Exceptions
-
type_error.304 if the JSON value is not an array; in this case, calling atwith an index makes no sense. See example below.out_of_range.401 if the index idx is out of range of the array; that is, idx >= size(). See example below.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 1.0.0
@liveexample{The example below shows how array elements can be read using at(). It also demonstrates the different exceptions that can be thrown., at__size_type_const}
Definition at line 20899 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), is_array(), JSON_CATCH, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, m_value, nlohmann::to_string(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ back() [1/2]
|
inline |
access the last element
Returns a reference to the last element in the container. For a JSON container c, the expression c.back() is equivalent to
- Returns
- In case of a structured type (array or object), a reference to the last element is returned. In case of number, string, boolean, or binary values, a reference to the value is returned.
@complexity Constant.
- Precondition
- The JSON value must not be
null(would throwstd::out_of_range) or an empty array or object (undefined behavior, guarded by assertions).
- Postcondition
- The JSON value remains unchanged.
- Exceptions
-
invalid_iterator.214 when called on a nullvalue. See example below.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for back().,back}
- See also
- see front() – access the first element
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21515 of file json.hpp.
References end(), and Ice::tmp.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ back() [2/2]
|
inline |
access the last element
Returns a reference to the last element in the container. For a JSON container c, the expression c.back() is equivalent to
- Returns
- In case of a structured type (array or object), a reference to the last element is returned. In case of number, string, boolean, or binary values, a reference to the value is returned.
@complexity Constant.
- Precondition
- The JSON value must not be
null(would throwstd::out_of_range) or an empty array or object (undefined behavior, guarded by assertions).
- Postcondition
- The JSON value remains unchanged.
- Exceptions
-
invalid_iterator.214 when called on a nullvalue. See example below.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for back().,back}
- See also
- see front() – access the first element
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21525 of file json.hpp.
References cend(), and Ice::tmp.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ begin() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const iterator to the first element
Returns a const iterator to the first element.
- Returns
- const iterator to the first element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).begin().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for cbegin().,cbegin}
- See also
- see begin() – returns an iterator to the beginning
- see end() – returns an iterator to the end
- see cend() – returns a const iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22046 of file json.hpp.
References cbegin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ begin() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns an iterator to the first element
Returns an iterator to the first element.
- Returns
- iterator to the first element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for begin().,begin}
- See also
- see cbegin() – returns a const iterator to the beginning
- see end() – returns an iterator to the end
- see cend() – returns a const iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22036 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by assert_invariant(), emplace(), front(), operator[](), and rend().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ binary() [1/4]
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create a binary array (without subtype)
Creates a JSON binary array value from a given binary container. Binary values are part of various binary formats, such as CBOR, MessagePack, and BSON. This constructor is used to create a value for serialization to those formats.
- Note
- Note, this function exists because of the difficulty in correctly specifying the correct template overload in the standard value ctor, as both JSON arrays and JSON binary arrays are backed with some form of a
std::vector. Because JSON binary arrays are a non-standard extension it was decided that it would be best to prevent automatic initialization of a binary array type, for backwards compatibility and so it does not happen on accident.
- Parameters
-
[in] init container containing bytes to use as binary type
- Returns
- JSON binary array value
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 19179 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, init(), and altar_valkyrie::res.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ binary() [2/4]
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create a binary array (with subtype)
Creates a JSON binary array value from a given binary container. Binary values are part of various binary formats, such as CBOR, MessagePack, and BSON. This constructor is used to create a value for serialization to those formats.
- Note
- Note, this function exists because of the difficulty in correctly specifying the correct template overload in the standard value ctor, as both JSON arrays and JSON binary arrays are backed with some form of a
std::vector. Because JSON binary arrays are a non-standard extension it was decided that it would be best to prevent automatic initialization of a binary array type, for backwards compatibility and so it does not happen on accident.
- Parameters
-
[in] init container containing bytes to use as binary type [in] subtype subtype to use in MessagePack and BSON
- Returns
- JSON binary array value
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 19216 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, init(), and altar_valkyrie::res.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ binary() [3/4]
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create a binary array (without subtype)
Creates a JSON binary array value from a given binary container. Binary values are part of various binary formats, such as CBOR, MessagePack, and BSON. This constructor is used to create a value for serialization to those formats.
- Note
- Note, this function exists because of the difficulty in correctly specifying the correct template overload in the standard value ctor, as both JSON arrays and JSON binary arrays are backed with some form of a
std::vector. Because JSON binary arrays are a non-standard extension it was decided that it would be best to prevent automatic initialization of a binary array type, for backwards compatibility and so it does not happen on accident.
- Parameters
-
[in] init container containing bytes to use as binary type
- Returns
- JSON binary array value
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 19226 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, init(), and altar_valkyrie::res.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ binary() [4/4]
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create a binary array (with subtype)
Creates a JSON binary array value from a given binary container. Binary values are part of various binary formats, such as CBOR, MessagePack, and BSON. This constructor is used to create a value for serialization to those formats.
- Note
- Note, this function exists because of the difficulty in correctly specifying the correct template overload in the standard value ctor, as both JSON arrays and JSON binary arrays are backed with some form of a
std::vector. Because JSON binary arrays are a non-standard extension it was decided that it would be best to prevent automatic initialization of a binary array type, for backwards compatibility and so it does not happen on accident.
- Parameters
-
[in] init container containing bytes to use as binary type [in] subtype subtype to use in MessagePack and BSON
- Returns
- JSON binary array value
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 19236 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, init(), and altar_valkyrie::res.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ cbegin()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const iterator to the first element
Returns a const iterator to the first element.
- Returns
- const iterator to the first element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).begin().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for cbegin().,cbegin}
- See also
- see begin() – returns an iterator to the beginning
- see end() – returns an iterator to the end
- see cend() – returns a const iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22076 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by begin(), crend(), front(), and update().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ cend()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const iterator to one past the last element
Returns a const iterator to one past the last element.
- Returns
- const iterator one past the last element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).end().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for cend().,cend}
- See also
- see end() – returns an iterator to the end
- see begin() – returns an iterator to the beginning
- see cbegin() – returns a const iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22147 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by back(), crbegin(), end(), find(), and update().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ clear()
|
inlinenoexcept |
clears the contents
Clears the content of a JSON value and resets it to the default value as if basic_json(value_t) would have been called with the current value type from type():
| Value type | initial value |
|---|---|
| null | null |
| boolean | false |
| string | "" |
| number | 0 |
| binary | An empty byte vector |
| object | {} |
| array | [] |
- Postcondition
- Has the same effect as calling
@liveexample{The example below shows the effect of clear() to different JSON types.,clear}
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value.
@iterators All iterators, pointers and references related to this container are invalidated.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
- See also
- see basic_json(value_t) – constructor that creates an object with the same value than calling
clear()
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22728 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
◆ contains() [1/2]
|
inline |
check the existence of an element in a JSON object given a JSON pointer
Check whether the given JSON pointer ptr can be resolved in the current JSON value.
- Note
- This method can be executed on any JSON value type.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr JSON pointer to check its existence.
- Returns
- true if the JSON pointer can be resolved to a stored value, false otherwise.
- Postcondition
- If
j.contains(ptr)returns true, it is safe to callj[ptr].
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.106 if an array index begins with '0' parse_error.109 if an array index was not a number
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the JSON object.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for contains().,contains_json_pointer}
- See also
- see contains(KeyT &&) const – checks the existence of a key
- Since
- version 3.7.0
◆ contains() [2/2]
|
inline |
check the existence of an element in a JSON object
Check whether an element exists in a JSON object with key equivalent to key. If the element is not found or the JSON value is not an object, false is returned.
- Note
- This method always returns false when executed on a JSON type that is not an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key value to check its existence.
- Returns
- true if an element with specified key exists. If no such element with such key is found or the JSON value is not an object, false is returned.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the JSON object.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for contains().,contains}
- See also
- see find(KeyT&&) – returns an iterator to an object element
- see contains(const json_pointer&) const – checks the existence for a JSON pointer
- Since
- version 3.6.0
Definition at line 21966 of file json.hpp.
References is_object(), and m_value.
Referenced by inja::Renderer::visit().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ count()
|
inline |
returns the number of occurrences of a key in a JSON object
Returns the number of elements with key key. If ObjectType is the default std::map type, the return value will always be 0 (key was not found) or 1 (key was found).
- Note
- This method always returns
0when executed on a JSON type that is not an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key value of the element to count
- Returns
- Number of elements with key key. If the JSON value is not an object, the return value will be
0.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the JSON object.
@liveexample{The example shows how count() is used.,count}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21933 of file json.hpp.
References is_object(), and m_value.
Referenced by set_parents().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ crbegin()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const reverse iterator to the last element
Returns a const iterator to the reverse-beginning; that is, the last element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).rbegin().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for crbegin().,crbegin}
- See also
- see rbegin() – returns a reverse iterator to the beginning
- see rend() – returns a reverse iterator to the end
- see crend() – returns a const reverse iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22251 of file json.hpp.
References cend().
Referenced by rbegin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ create()
|
inlinestaticprivate |
helper for exception-safe object creation
Definition at line 18310 of file json.hpp.
References make_face_from_files::args, JSON_ASSERT, and altar_valkyrie::obj.
◆ crend()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const reverse iterator to one before the first
Returns a const reverse iterator to the reverse-end; that is, one before the first element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).rend().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for crend().,crend}
- See also
- see rend() – returns a reverse iterator to the end
- see rbegin() – returns a reverse iterator to the beginning
- see crbegin() – returns a const reverse iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22280 of file json.hpp.
References cbegin().
Referenced by rend().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ destroy()
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 18516 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, array, nlohmann::detail::binary, binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, nlohmann::detail::string, and Floor::t.
Referenced by erase().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ diff()
|
inlinestatic |
creates a diff as a JSON patch
Creates a JSON Patch so that value source can be changed into the value target by calling patch function.
- Invariant
- For two JSON values source and target, the following code yields always
true:source.patch(diff(source, target)) == target;
- Note
- Currently, only
remove,add, andreplaceoperations are generated.
- Parameters
-
[in] source JSON value to compare from [in] target JSON value to compare against [in] path helper value to create JSON pointers
- Returns
- a JSON patch to convert the source to target
@complexity Linear in the lengths of source and target.
@liveexample{The following code shows how a JSON patch is created as a diff for two JSON values.,diff}
- See also
- see patch – apply a JSON patch
- see merge_patch – apply a JSON Merge Patch
- RFC 6902 (JSON Patch)
- Since
- version 2.0.0
Definition at line 26097 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::escape(), nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, object(), python_init::path, rotate-tower::result, nlohmann::detail::string, and nlohmann::to_string().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ dump()
|
inline |
serialization
Serialization function for JSON values. The function tries to mimic Python's json.dumps() function, and currently supports its indent and ensure_ascii parameters.
- Parameters
-
[in] indent If indent is nonnegative, then array elements and object members will be pretty-printed with that indent level. An indent level of 0will only insert newlines.-1(the default) selects the most compact representation.[in] indent_char The character to use for indentation if indent is greater than 0. The default is (space).[in] ensure_ascii If ensure_ascii is true, all non-ASCII characters in the output are escaped with \uXXXXsequences, and the result consists of ASCII characters only.[in] error_handler how to react on decoding errors; there are three possible values: strict(throws and exception in case a decoding error occurs; default),replace(replace invalid UTF-8 sequences with U+FFFD), andignore(ignore invalid UTF-8 sequences during serialization; all bytes are copied to the output unchanged).
- Returns
- string containing the serialization of the JSON value
- Exceptions
-
type_error.316 if a string stored inside the JSON value is not UTF-8 encoded and error_handler is set to strict
- Note
- Binary values are serialized as object containing two keys:
- "bytes": an array of bytes as integers
- "subtype": the subtype as integer or "null" if the binary has no subtype
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@liveexample{The following example shows the effect of different indent\, indent_char\, and ensure_ascii parameters to the result of the serialization.,dump}
- Since
- version 1.0.0; indentation character indent_char, option ensure_ascii and exceptions added in version 3.0.0; error handlers added in version 3.4.0; serialization of binary values added in version 3.8.0.
Definition at line 19784 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
◆ emplace()
|
inline |
add an object to an object if key does not exist
Inserts a new element into a JSON object constructed in-place with the given args if there is no element with the key in the container. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty object is created before appending the value created from args.
- Parameters
-
[in] args arguments to forward to a constructor of basic_json
- Template Parameters
-
Args compatible types to create a basic_json object
- Returns
- a pair consisting of an iterator to the inserted element, or the already-existing element if no insertion happened, and a bool denoting whether the insertion took place.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.311 when called on a type other than JSON object or null; example: "cannot use emplace() with number"
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container, O(log(size())).
@liveexample{The example shows how emplace() can be used to add elements to a JSON object. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON object. Further note how no value is added if there was already one value stored with the same key.,emplace}
- Since
- version 2.0.8
Definition at line 23050 of file json.hpp.
References make_face_from_files::args, assert_invariant(), begin(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, altar_valkyrie::res, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ emplace_back()
|
inline |
add an object to an array
Creates a JSON value from the passed parameters args to the end of the JSON value. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty array is created before appending the value created from args.
- Parameters
-
[in] args arguments to forward to a constructor of basic_json
- Template Parameters
-
Args compatible types to create a basic_json object
- Returns
- reference to the inserted element
- Exceptions
-
type_error.311 when called on a type other than JSON array or null; example: "cannot use emplace_back() with number"
@complexity Amortized constant.
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() can be used to add elements to a JSON array. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON array.,emplace_back}
- Since
- version 2.0.8, returns reference since 3.7.0
Definition at line 23000 of file json.hpp.
References make_face_from_files::args, nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), is_null(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, set_parent(), and type_name().
Referenced by inja::Renderer::render_to().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ empty()
|
inlinenoexcept |
checks whether the container is empty.
Checks if a JSON value has no elements (i.e. whether its size is 0).
- Returns
- The return value depends on the different types and is defined as follows:
Value type return value null trueboolean falsestring falsenumber falsebinary falseobject result of function object_t::empty()array result of function array_t::empty()
@liveexample{The following code uses empty() to check if a JSON object contains any elements.,empty}
@complexity Constant, as long as array_t and object_t satisfy the Container concept; that is, their empty() functions have constant complexity.
@iterators No changes.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
- Note
- This function does not return whether a string stored as JSON value is empty - it returns whether the JSON container itself is empty which is false in the case of a string.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- See also
- see size() – returns the number of elements
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22491 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by inja::Renderer::visit().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ end() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const iterator to one past the last element
Returns a const iterator to one past the last element.
- Returns
- const iterator one past the last element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).end().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for cend().,cend}
- See also
- see end() – returns an iterator to the end
- see begin() – returns an iterator to the beginning
- see cbegin() – returns a const iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22117 of file json.hpp.
References cend().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ end() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns an iterator to one past the last element
Returns an iterator to one past the last element.
- Returns
- iterator one past the last element
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for end().,end}
- See also
- see cend() – returns a const iterator to the end
- see begin() – returns an iterator to the beginning
- see cbegin() – returns a const iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22107 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by assert_invariant(), back(), erase(), find(), rbegin(), and value().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ erase() [1/4]
|
inline |
remove element from a JSON array given an index
Removes element from a JSON array at the index idx.
- Parameters
-
[in] idx index of the element to remove
- Exceptions
-
type_error.307 when called on a type other than JSON object; example: "cannot use erase() with null"out_of_range.401 when idx >= size(); example:"array index 17 is out of range"
@complexity Linear in distance between idx and the end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows the effect of erase().,erase__size_type}
- See also
- see erase(IteratorType) – removes the element at a given position
- see erase(IteratorType, IteratorType) – removes the elements in the given range
- see erase(const typename object_t::key_type&) – removes the element from an object at the given key
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21829 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, size(), nlohmann::to_string(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ erase() [2/4]
|
inline |
remove element from a JSON object given a key
Removes elements from a JSON object with the key value key.
- Parameters
-
[in] key value of the elements to remove
- Returns
- Number of elements removed. If ObjectType is the default
std::maptype, the return value will always be0(key was not found) or1(key was found).
- Postcondition
- References and iterators to the erased elements are invalidated. Other references and iterators are not affected.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.307 when called on a type other than JSON object; example: "cannot use erase() with null"
@complexity log(size()) + count(key)
@liveexample{The example shows the effect of erase().,erase__key_type}
- See also
- see erase(IteratorType) – removes the element at a given position
- see erase(IteratorType, IteratorType) – removes the elements in the given range
- see erase(const size_type) – removes the element from an array at the given index
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21794 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ erase() [3/4]
|
inline |
remove elements given an iterator range
Removes the element specified by the range [first; last). The iterator first does not need to be dereferenceable if first == last: erasing an empty range is a no-op.
If called on a primitive type other than null, the resulting JSON value will be null.
- Parameters
-
[in] first iterator to the beginning of the range to remove [in] last iterator past the end of the range to remove
- Returns
- Iterator following the last removed element. If the iterator second refers to the last element, the
end()iterator is returned.
- Template Parameters
-
IteratorType an iterator or const_iterator
- Postcondition
- Invalidates iterators and references at or after the point of the erase, including the
end()iterator.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.307 if called on a nullvalue; example:"cannot use erase() with null"invalid_iterator.203 if called on iterators which does not belong to the current JSON value; example: "iterators do not fit current value"invalid_iterator.204 if called on a primitive type with invalid iterators (i.e., if first != begin()andlast != end()); example:"iterators out of range"
@complexity The complexity depends on the type:
- objects:
log(size()) + std::distance(first, last) - arrays: linear in the distance between first and last, plus linear in the distance between last and end of the container
- strings and binary: linear in the length of the member
- other types: constant
@liveexample{The example shows the result of erase() for different JSON types.,erase__IteratorType_IteratorType}
- See also
- see erase(IteratorType) – removes the element at a given position
- see erase(const typename object_t::key_type&) – removes the element from an object at the given key
- see erase(const size_type) – removes the element from an array at the given index
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21697 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), destroy(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, end(), is_binary(), is_string(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, rotate-tower::result, nlohmann::detail::string, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ erase() [4/4]
|
inline |
remove element given an iterator
Removes the element specified by iterator pos. The iterator pos must be valid and dereferenceable. Thus the end() iterator (which is valid, but is not dereferenceable) cannot be used as a value for pos.
If called on a primitive type other than null, the resulting JSON value will be null.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator to the element to remove
- Returns
- Iterator following the last removed element. If the iterator pos refers to the last element, the
end()iterator is returned.
- Template Parameters
-
IteratorType an iterator or const_iterator
- Postcondition
- Invalidates iterators and references at or after the point of the erase, including the
end()iterator.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.307 if called on a nullvalue; example:"cannot use erase() with null"invalid_iterator.202 if called on an iterator which does not belong to the current JSON value; example: "iterator does not fit current value"invalid_iterator.205 if called on a primitive type with invalid iterator (i.e., any iterator which is not begin()); example:"iterator out of range"
@complexity The complexity depends on the type:
- objects: amortized constant
- arrays: linear in distance between pos and the end of the container
- strings and binary: linear in the length of the member
- other types: constant
@liveexample{The example shows the result of erase() for different JSON types.,erase__IteratorType}
- See also
- see erase(IteratorType, IteratorType) – removes the elements in the given range
- see erase(const typename object_t::key_type&) – removes the element from an object at the given key
- see erase(const size_type) – removes the element from an array at the given index
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21582 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), destroy(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, end(), is_binary(), is_string(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, rotate-tower::result, nlohmann::detail::string, and type_name().
Referenced by main(), and merge_patch().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ find() [1/2]
|
inline |
find an element in a JSON object
Finds an element in a JSON object with key equivalent to key. If the element is not found or the JSON value is not an object, end() is returned.
- Note
- This method always returns end() when executed on a JSON type that is not an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key value of the element to search for.
- Returns
- Iterator to an element with key equivalent to key. If no such element is found or the JSON value is not an object, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the JSON object.
@liveexample{The example shows how find() is used.,find__key_type}
- See also
- see contains(KeyT&&) const – checks whether a key exists
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21882 of file json.hpp.
References end(), is_object(), m_value, and rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by value().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ find() [2/2]
|
inline |
find an element in a JSON object
find an element in a JSON object Finds an element in a JSON object with key equivalent to key. If the element is not found or the JSON value is not an object, end() is returned.
- Note
- This method always returns end() when executed on a JSON type that is not an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key value of the element to search for.
- Returns
- Iterator to an element with key equivalent to key. If no such element is found or the JSON value is not an object, past-the-end (see end()) iterator is returned.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the JSON object.
@liveexample{The example shows how find() is used.,find__key_type}
- See also
- see contains(KeyT&&) const – checks whether a key exists
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21899 of file json.hpp.
References cend(), is_object(), m_value, and rotate-tower::result.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ flatten()
|
inline |
return flattened JSON value
The function creates a JSON object whose keys are JSON pointers (see RFC 6901) and whose values are all primitive. The original JSON value can be restored using the unflatten() function.
- Returns
- an object that maps JSON pointers to primitive values
- Note
- Empty objects and arrays are flattened to
nulland will not be reconstructed correctly by the unflatten() function.
@complexity Linear in the size the JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows how a JSON object is flattened to an object whose keys consist of JSON pointers.,flatten}
- See also
- see unflatten() for the reverse function
- Since
- version 2.0.0
Definition at line 25693 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::json_pointer< BasicJsonType >::flatten(), nlohmann::detail::object, and rotate-tower::result.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_bson() [1/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25490 of file json.hpp.
References from_bson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_bson() [2/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25499 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_bson() [3/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Create a JSON value from an input in BSON format.
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the BSON (Binary JSON) serialization format.
The library maps BSON record types to JSON value types as follows:
| BSON type | BSON marker byte | JSON value type |
|---|---|---|
| double | 0x01 | number_float |
| string | 0x02 | string |
| document | 0x03 | object |
| array | 0x04 | array |
| binary | 0x05 | binary |
| undefined | 0x06 | still unsupported |
| ObjectId | 0x07 | still unsupported |
| boolean | 0x08 | boolean |
| UTC Date-Time | 0x09 | still unsupported |
| null | 0x0A | null |
| Regular Expr. | 0x0B | still unsupported |
| DB Pointer | 0x0C | still unsupported |
| JavaScript Code | 0x0D | still unsupported |
| Symbol | 0x0E | still unsupported |
| JavaScript Code | 0x0F | still unsupported |
| int32 | 0x10 | number_integer |
| Timestamp | 0x11 | still unsupported |
| 128-bit decimal float | 0x13 | still unsupported |
| Max Key | 0x7F | still unsupported |
| Min Key | 0xFF | still unsupported |
- Warning
- The mapping is incomplete. The unsupported mappings are indicated in the table above.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in BSON format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.114 if an unsupported BSON record type is encountered
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in BSON format to a JSON value.,from_bson}
- See also
- http://bsonspec.org/spec.html
- see to_bson(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
Definition at line 25460 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
Referenced by from_bson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ from_bson() [4/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Create a JSON value from an input in BSON format.
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the BSON (Binary JSON) serialization format.
The library maps BSON record types to JSON value types as follows:
| BSON type | BSON marker byte | JSON value type |
|---|---|---|
| double | 0x01 | number_float |
| string | 0x02 | string |
| document | 0x03 | object |
| array | 0x04 | array |
| binary | 0x05 | binary |
| undefined | 0x06 | still unsupported |
| ObjectId | 0x07 | still unsupported |
| boolean | 0x08 | boolean |
| UTC Date-Time | 0x09 | still unsupported |
| null | 0x0A | null |
| Regular Expr. | 0x0B | still unsupported |
| DB Pointer | 0x0C | still unsupported |
| JavaScript Code | 0x0D | still unsupported |
| Symbol | 0x0E | still unsupported |
| JavaScript Code | 0x0F | still unsupported |
| int32 | 0x10 | number_integer |
| Timestamp | 0x11 | still unsupported |
| 128-bit decimal float | 0x13 | still unsupported |
| Max Key | 0x7F | still unsupported |
| Min Key | 0xFF | still unsupported |
- Warning
- The mapping is incomplete. The unsupported mappings are indicated in the table above.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in BSON format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.114 if an unsupported BSON record type is encountered
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in BSON format to a JSON value.,from_bson}
- See also
- http://bsonspec.org/spec.html
- see to_bson(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
Definition at line 25476 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_cbor() [1/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25117 of file json.hpp.
References from_cbor().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_cbor() [2/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25128 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_cbor() [3/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in CBOR format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the CBOR (Concise Binary Object Representation) serialization format.
The library maps CBOR types to JSON value types as follows:
| CBOR type | JSON value type | first byte |
|---|---|---|
| Integer | number_unsigned | 0x00..0x17 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x18 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x19 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x1A |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x1B |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x20..0x37 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x38 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x39 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x3A |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x3B |
| Byte string | binary | 0x40..0x57 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x58 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x59 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x5A |
| Byte string | binary | 0x5B |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x60..0x77 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x78 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x79 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7A |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7B |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7F |
| array | array | 0x80..0x97 |
| array | array | 0x98 |
| array | array | 0x99 |
| array | array | 0x9A |
| array | array | 0x9B |
| array | array | 0x9F |
| map | object | 0xA0..0xB7 |
| map | object | 0xB8 |
| map | object | 0xB9 |
| map | object | 0xBA |
| map | object | 0xBB |
| map | object | 0xBF |
| False | false | 0xF4 |
| True | true | 0xF5 |
| Null | null | 0xF6 |
| Half-Precision Float | number_float | 0xF9 |
| Single-Precision Float | number_float | 0xFA |
| Double-Precision Float | number_float | 0xFB |
- Warning
- The mapping is incomplete in the sense that not all CBOR types can be converted to a JSON value. The following CBOR types are not supported and will yield parse errors (parse_error.112):
- date/time (0xC0..0xC1)
- bignum (0xC2..0xC3)
- decimal fraction (0xC4)
- bigfloat (0xC5)
- expected conversions (0xD5..0xD7)
- simple values (0xE0..0xF3, 0xF8)
- undefined (0xF7)
- CBOR allows map keys of any type, whereas JSON only allows strings as keys in object values. Therefore, CBOR maps with keys other than UTF-8 strings are rejected (parse_error.113).
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in CBOR format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default) [in] tag_handler how to treat CBOR tags (optional, error by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if unsupported features from CBOR were used in the given input v or if the input is not valid CBOR parse_error.113 if a string was expected as map key, but not found
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in CBOR format to a JSON value.,from_cbor}
- See also
- http://cbor.io
- see to_cbor(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9; parameter start_index since 2.1.1; changed to consume input adapters, removed start_index parameter, and added strict parameter since 3.0.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0; added tag_handler parameter since 3.9.0.
Definition at line 25085 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
Referenced by from_cbor().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ from_cbor() [4/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in CBOR format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the CBOR (Concise Binary Object Representation) serialization format.
The library maps CBOR types to JSON value types as follows:
| CBOR type | JSON value type | first byte |
|---|---|---|
| Integer | number_unsigned | 0x00..0x17 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x18 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x19 |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x1A |
| Unsigned integer | number_unsigned | 0x1B |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x20..0x37 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x38 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x39 |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x3A |
| Negative integer | number_integer | 0x3B |
| Byte string | binary | 0x40..0x57 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x58 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x59 |
| Byte string | binary | 0x5A |
| Byte string | binary | 0x5B |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x60..0x77 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x78 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x79 |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7A |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7B |
| UTF-8 string | string | 0x7F |
| array | array | 0x80..0x97 |
| array | array | 0x98 |
| array | array | 0x99 |
| array | array | 0x9A |
| array | array | 0x9B |
| array | array | 0x9F |
| map | object | 0xA0..0xB7 |
| map | object | 0xB8 |
| map | object | 0xB9 |
| map | object | 0xBA |
| map | object | 0xBB |
| map | object | 0xBF |
| False | false | 0xF4 |
| True | true | 0xF5 |
| Null | null | 0xF6 |
| Half-Precision Float | number_float | 0xF9 |
| Single-Precision Float | number_float | 0xFA |
| Double-Precision Float | number_float | 0xFB |
- Warning
- The mapping is incomplete in the sense that not all CBOR types can be converted to a JSON value. The following CBOR types are not supported and will yield parse errors (parse_error.112):
- date/time (0xC0..0xC1)
- bignum (0xC2..0xC3)
- decimal fraction (0xC4)
- bigfloat (0xC5)
- expected conversions (0xD5..0xD7)
- simple values (0xE0..0xF3, 0xF8)
- undefined (0xF7)
- CBOR allows map keys of any type, whereas JSON only allows strings as keys in object values. Therefore, CBOR maps with keys other than UTF-8 strings are rejected (parse_error.113).
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in CBOR format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default) [in] tag_handler how to treat CBOR tags (optional, error by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if unsupported features from CBOR were used in the given input v or if the input is not valid CBOR parse_error.113 if a string was expected as map key, but not found
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in CBOR format to a JSON value.,from_cbor}
- See also
- http://cbor.io
- see to_cbor(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9; parameter start_index since 2.1.1; changed to consume input adapters, removed start_index parameter, and added strict parameter since 3.0.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0; added tag_handler parameter since 3.9.0.
Definition at line 25102 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_msgpack() [1/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25260 of file json.hpp.
References from_msgpack().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_msgpack() [2/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25269 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_msgpack() [3/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in MessagePack format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the MessagePack serialization format.
The library maps MessagePack types to JSON value types as follows:
| MessagePack type | JSON value type | first byte |
|---|---|---|
| positive fixint | number_unsigned | 0x00..0x7F |
| fixmap | object | 0x80..0x8F |
| fixarray | array | 0x90..0x9F |
| fixstr | string | 0xA0..0xBF |
| nil | null | 0xC0 |
| false | false | 0xC2 |
| true | true | 0xC3 |
| float 32 | number_float | 0xCA |
| float 64 | number_float | 0xCB |
| uint 8 | number_unsigned | 0xCC |
| uint 16 | number_unsigned | 0xCD |
| uint 32 | number_unsigned | 0xCE |
| uint 64 | number_unsigned | 0xCF |
| int 8 | number_integer | 0xD0 |
| int 16 | number_integer | 0xD1 |
| int 32 | number_integer | 0xD2 |
| int 64 | number_integer | 0xD3 |
| str 8 | string | 0xD9 |
| str 16 | string | 0xDA |
| str 32 | string | 0xDB |
| array 16 | array | 0xDC |
| array 32 | array | 0xDD |
| map 16 | object | 0xDE |
| map 32 | object | 0xDF |
| bin 8 | binary | 0xC4 |
| bin 16 | binary | 0xC5 |
| bin 32 | binary | 0xC6 |
| ext 8 | binary | 0xC7 |
| ext 16 | binary | 0xC8 |
| ext 32 | binary | 0xC9 |
| fixext 1 | binary | 0xD4 |
| fixext 2 | binary | 0xD5 |
| fixext 4 | binary | 0xD6 |
| fixext 8 | binary | 0xD7 |
| fixext 16 | binary | 0xD8 |
| negative fixint | number_integer | 0xE0-0xFF |
- Note
- Any MessagePack output created to_msgpack can be successfully parsed by from_msgpack.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in MessagePack format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if unsupported features from MessagePack were used in the given input i or if the input is not valid MessagePack parse_error.113 if a string was expected as map key, but not found
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in MessagePack format to a JSON value.,from_msgpack}
- See also
- http://msgpack.org
- see to_msgpack(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- see from_bson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related BSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9; parameter start_index since 2.1.1; changed to consume input adapters, removed start_index parameter, and added strict parameter since 3.0.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0
Definition at line 25229 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
Referenced by from_msgpack().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ from_msgpack() [4/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in MessagePack format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the MessagePack serialization format.
The library maps MessagePack types to JSON value types as follows:
| MessagePack type | JSON value type | first byte |
|---|---|---|
| positive fixint | number_unsigned | 0x00..0x7F |
| fixmap | object | 0x80..0x8F |
| fixarray | array | 0x90..0x9F |
| fixstr | string | 0xA0..0xBF |
| nil | null | 0xC0 |
| false | false | 0xC2 |
| true | true | 0xC3 |
| float 32 | number_float | 0xCA |
| float 64 | number_float | 0xCB |
| uint 8 | number_unsigned | 0xCC |
| uint 16 | number_unsigned | 0xCD |
| uint 32 | number_unsigned | 0xCE |
| uint 64 | number_unsigned | 0xCF |
| int 8 | number_integer | 0xD0 |
| int 16 | number_integer | 0xD1 |
| int 32 | number_integer | 0xD2 |
| int 64 | number_integer | 0xD3 |
| str 8 | string | 0xD9 |
| str 16 | string | 0xDA |
| str 32 | string | 0xDB |
| array 16 | array | 0xDC |
| array 32 | array | 0xDD |
| map 16 | object | 0xDE |
| map 32 | object | 0xDF |
| bin 8 | binary | 0xC4 |
| bin 16 | binary | 0xC5 |
| bin 32 | binary | 0xC6 |
| ext 8 | binary | 0xC7 |
| ext 16 | binary | 0xC8 |
| ext 32 | binary | 0xC9 |
| fixext 1 | binary | 0xD4 |
| fixext 2 | binary | 0xD5 |
| fixext 4 | binary | 0xD6 |
| fixext 8 | binary | 0xD7 |
| fixext 16 | binary | 0xD8 |
| negative fixint | number_integer | 0xE0-0xFF |
- Note
- Any MessagePack output created to_msgpack can be successfully parsed by from_msgpack.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in MessagePack format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if unsupported features from MessagePack were used in the given input i or if the input is not valid MessagePack parse_error.113 if a string was expected as map key, but not found
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in MessagePack format to a JSON value.,from_msgpack}
- See also
- http://msgpack.org
- see to_msgpack(const basic_json&) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- see from_bson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related BSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9; parameter start_index since 2.1.1; changed to consume input adapters, removed start_index parameter, and added strict parameter since 3.0.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0
Definition at line 25245 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_ubjson() [1/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25376 of file json.hpp.
References from_ubjson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_ubjson() [2/4]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 25385 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ from_ubjson() [3/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in UBJSON format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the UBJSON (Universal Binary JSON) serialization format.
The library maps UBJSON types to JSON value types as follows:
| UBJSON type | JSON value type | marker |
|---|---|---|
| no-op | no value, next value is read | N |
| null | null | Z |
| false | false | F |
| true | true | T |
| float32 | number_float | d |
| float64 | number_float | D |
| uint8 | number_unsigned | U |
| int8 | number_integer | i |
| int16 | number_integer | I |
| int32 | number_integer | l |
| int64 | number_integer | L |
| high-precision number | number_integer, number_unsigned, or number_float - depends on number string | 'H' |
| string | string | S |
| char | string | C |
| array | array (optimized values are supported) | [ |
| object | object (optimized values are supported) | { |
- Note
- The mapping is complete in the sense that any UBJSON value can be converted to a JSON value.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in UBJSON format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if a parse error occurs parse_error.113 if a string could not be parsed successfully
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in UBJSON format to a JSON value.,from_ubjson}
- See also
- http://ubjson.org
- see to_ubjson(const basic_json&, const bool, const bool) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_bson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related BSON format
- Since
- version 3.1.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0
Definition at line 25346 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
Referenced by from_ubjson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ from_ubjson() [4/4]
|
inlinestatic |
create a JSON value from an input in UBJSON format
Deserializes a given input i to a JSON value using the UBJSON (Universal Binary JSON) serialization format.
The library maps UBJSON types to JSON value types as follows:
| UBJSON type | JSON value type | marker |
|---|---|---|
| no-op | no value, next value is read | N |
| null | null | Z |
| false | false | F |
| true | true | T |
| float32 | number_float | d |
| float64 | number_float | D |
| uint8 | number_unsigned | U |
| int8 | number_integer | i |
| int16 | number_integer | I |
| int32 | number_integer | l |
| int64 | number_integer | L |
| high-precision number | number_integer, number_unsigned, or number_float - depends on number string | 'H' |
| string | string | S |
| char | string | C |
| array | array (optimized values are supported) | [ |
| object | object (optimized values are supported) | { |
- Note
- The mapping is complete in the sense that any UBJSON value can be converted to a JSON value.
- Parameters
-
[in] i an input in UBJSON format convertible to an input adapter [in] strict whether to expect the input to be consumed until EOF (true by default) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.110 if the given input ends prematurely or the end of file was not reached when strict was set to true parse_error.112 if a parse error occurs parse_error.113 if a string could not be parsed successfully
@complexity Linear in the size of the input i.
@liveexample{The example shows the deserialization of a byte vector in UBJSON format to a JSON value.,from_ubjson}
- See also
- http://ubjson.org
- see to_ubjson(const basic_json&, const bool, const bool) for the analogous serialization
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the related CBOR format
- see from_msgpack(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related MessagePack format
- see from_bson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the related BSON format
- Since
- version 3.1.0; added allow_exceptions parameter since 3.2.0
Definition at line 25362 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), altar_valkyrie::res, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ front() [1/2]
|
inline |
access the first element
Returns a reference to the first element in the container. For a JSON container c, the expression c.front() is equivalent to *c.begin().
- Returns
- In case of a structured type (array or object), a reference to the first element is returned. In case of number, string, boolean, or binary values, a reference to the value is returned.
@complexity Constant.
- Precondition
- The JSON value must not be
null(would throwstd::out_of_range) or an empty array or object (undefined behavior, guarded by assertions).
- Postcondition
- The JSON value remains unchanged.
- Exceptions
-
invalid_iterator.214 when called on nullvalue
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for front().,front}
- See also
- see back() – access the last element
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21471 of file json.hpp.
References begin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ front() [2/2]
|
inline |
access the first element
Returns a reference to the first element in the container. For a JSON container c, the expression c.front() is equivalent to *c.begin().
- Returns
- In case of a structured type (array or object), a reference to the first element is returned. In case of number, string, boolean, or binary values, a reference to the value is returned.
@complexity Constant.
- Precondition
- The JSON value must not be
null(would throwstd::out_of_range) or an empty array or object (undefined behavior, guarded by assertions).
- Postcondition
- The JSON value remains unchanged.
- Exceptions
-
invalid_iterator.214 when called on nullvalue
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for front().,front}
- See also
- see back() – access the last element
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21479 of file json.hpp.
References cbegin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
get a (pointer) value (explicit)
Performs explicit type conversion between the JSON value and a compatible value if required.
- If the requested type is a pointer to the internally stored JSON value that pointer is returned. No copies are made.
- If the requested type is the current basic_json, or a different basic_json convertible from the current basic_json.
- Otherwise the value is converted by calling the json_serializer<ValueType>
from_json()method.
- Template Parameters
-
ValueTypeCV the provided value type ValueType the returned value type
- Returns
- copy of the JSON value, converted to
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType if necessary
- Exceptions
-
what json_serializer<ValueType> from_json()method throws if conversion is required
- Since
- version 2.1.0
◆ get() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
get a pointer value (explicit)
Explicit pointer access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- The pointer becomes invalid if the underlying JSON object changes.
- Template Parameters
-
PointerType pointer type; must be a pointer to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t, or number_float_t.
- Returns
- pointer to the internally stored JSON value if the requested pointer type PointerType fits to the JSON value;
nullptrotherwise
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how pointers to internal values of a JSON value can be requested. Note that no type conversions are made and a nullptr is returned if the value and the requested pointer type does not match.,get__PointerType}
- See also
- see get_ptr() for explicit pointer-member access
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ get_allocator()
|
inlinestatic |
◆ get_binary() [1/2]
|
inline |
- Returns
- reference to the binary value
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 if the value is not binary
- See also
- see is_binary() to check if the value is binary
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 20794 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_binary(), JSON_THROW, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_binary() [2/2]
|
inline |
- Returns
- reference to the binary value
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 if the value is not binary
- See also
- see is_binary() to check if the value is binary
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 20805 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_binary(), JSON_THROW, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl() [1/7]
get a boolean (explicit)
Definition at line 20208 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_boolean(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl() [2/7]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
get a value (explicit)
Explicit type conversion between the JSON value and a compatible value which is CopyConstructible and DefaultConstructible. The value is converted by calling the json_serializer<ValueType> from_json() method.
The function is equivalent to executing
This overloads is chosen if:
- ValueType is not basic_json,
- json_serializer<ValueType> has a
from_json()method of the formvoid from_json(const basic_json&, ValueType&), and - json_serializer<ValueType> does not have a
from_json()method of the formValueType from_json(const basic_json&)
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType the returned value type
- Returns
- copy of the JSON value, converted to ValueType
- Exceptions
-
what json_serializer<ValueType> from_json()method throws
@liveexample{The example below shows several conversions from JSON values to other types. There a few things to note: (1) Floating-point numbers can be converted to integers\, (2) A JSON array can be converted to a standard std::vector<short>\, (3) A JSON object can be converted to C++ associative containers such as std::unordered_map<std::string\, json>.,get__ValueType_const}
- Since
- version 2.1.0
Definition at line 20435 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::from_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl() [3/7]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
get a value (explicit); special case
Explicit type conversion between the JSON value and a compatible value which is not CopyConstructible and not DefaultConstructible. The value is converted by calling the json_serializer<ValueType> from_json() method.
The function is equivalent to executing
This overloads is chosen if:
- ValueType is not basic_json and
- json_serializer<ValueType> has a
from_json()method of the formValueType from_json(const basic_json&)
- Note
- If json_serializer<ValueType> has both overloads of
from_json(), this one is chosen.
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType the returned value type
- Returns
- copy of the JSON value, converted to ValueType
- Exceptions
-
what json_serializer<ValueType> from_json()method throws
- Since
- version 2.1.0
Definition at line 20477 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::from_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl() [4/7]
|
inlineprivate |
get special-case overload
This overloads converts the current basic_json in a different basic_json type
- Template Parameters
-
BasicJsonType == basic_json
- Returns
- a copy of *this, converted into BasicJsonType
@complexity Depending on the implementation of the called from_json() method.
- Since
- version 3.2.0
◆ get_impl() [5/7]
|
inlineprivate |
get special-case overload
This overloads avoids a lot of template boilerplate, it can be seen as the identity method
- Template Parameters
-
BasicJsonType == basic_json
- Returns
- a copy of *this
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 2.1.0
◆ get_impl() [6/7]
| return nlohmann::basic_json::get_impl | ( | detail::priority_tag< 4 > {} | ) |
◆ get_impl() [7/7]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer value (explicit)
get a pointer value (explicit) Explicit pointer access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- The pointer becomes invalid if the underlying JSON object changes.
- Template Parameters
-
PointerType pointer type; must be a pointer to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t, or number_float_t.
- Returns
- pointer to the internally stored JSON value if the requested pointer type PointerType fits to the JSON value;
nullptrotherwise
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how pointers to internal values of a JSON value can be requested. Note that no type conversions are made and a nullptr is returned if the value and the requested pointer type does not match.,get__PointerType}
- See also
- see get_ptr() for explicit pointer-member access
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ get_impl_ptr() [1/16]
get a pointer to the value (array)
Definition at line 20231 of file json.hpp.
References is_array(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [2/16]
get a pointer to the value (binary)
Definition at line 20303 of file json.hpp.
References is_binary(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [3/16]
get a pointer to the value (boolean)
Definition at line 20255 of file json.hpp.
References is_boolean(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [4/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (array)
Definition at line 20237 of file json.hpp.
References is_array(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [5/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (binary)
Definition at line 20309 of file json.hpp.
References is_binary(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [6/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (boolean)
Definition at line 20261 of file json.hpp.
References is_boolean(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [7/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (floating-point number)
Definition at line 20297 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_float(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [8/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (integer number)
Definition at line 20273 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_integer(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [9/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (unsigned number)
Definition at line 20285 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_unsigned(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [10/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (object)
Definition at line 20225 of file json.hpp.
References is_object(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [11/16]
|
inlineconstexprprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (string)
Definition at line 20249 of file json.hpp.
References is_string(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [12/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (floating-point number)
Definition at line 20291 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_float(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [13/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (integer number)
Definition at line 20267 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_integer(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [14/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
get a pointer to the value (unsigned number)
Definition at line 20279 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_unsigned(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [15/16]
get a pointer to the value (object)
Definition at line 20219 of file json.hpp.
References is_object(), and m_value.
Referenced by get_ptr().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ get_impl_ptr() [16/16]
get a pointer to the value (string)
Definition at line 20243 of file json.hpp.
References is_string(), and m_value.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_ptr() [1/2]
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
get a pointer value (implicit)
get a pointer value (implicit) Implicit pointer access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- Writing data to the pointee of the result yields an undefined state.
- Template Parameters
-
PointerType pointer type; must be a pointer to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t, or number_float_t. Enforced by a static assertion.
- Returns
- pointer to the internally stored JSON value if the requested pointer type PointerType fits to the JSON value;
nullptrotherwise
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how pointers to internal values of a JSON value can be requested. Note that no type conversions are made and a nullptr is returned if the value and the requested pointer type does not match.,get_ptr}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20385 of file json.hpp.
References get_impl_ptr().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_ptr() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
get a pointer value (implicit)
Implicit pointer access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- Writing data to the pointee of the result yields an undefined state.
- Template Parameters
-
PointerType pointer type; must be a pointer to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, number_unsigned_t, or number_float_t. Enforced by a static assertion.
- Returns
- pointer to the internally stored JSON value if the requested pointer type PointerType fits to the JSON value;
nullptrotherwise
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how pointers to internal values of a JSON value can be requested. Note that no type conversions are made and a nullptr is returned if the value and the requested pointer type does not match.,get_ptr}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20372 of file json.hpp.
References get_impl_ptr().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_ref() [1/2]
|
inline |
get a reference value (implicit)
Implicit reference access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- Writing data to the referee of the result yields an undefined state.
- Template Parameters
-
ReferenceType reference type; must be a reference to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, or number_float_t. Enforced by static assertion.
- Returns
- reference to the internally stored JSON value if the requested reference type ReferenceType fits to the JSON value; throws type_error.303 otherwise
- Exceptions
-
type_error.303 in case passed type ReferenceType is incompatible with the stored JSON value; see example below
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example shows several calls to get_ref().,get_ref}
- Since
- version 1.1.0
◆ get_ref() [2/2]
|
inline |
get a reference value (implicit)
get a reference value (implicit) Implicit reference access to the internally stored JSON value. No copies are made.
- Warning
- Writing data to the referee of the result yields an undefined state.
- Template Parameters
-
ReferenceType reference type; must be a reference to array_t, object_t, string_t, boolean_t, number_integer_t, or number_float_t. Enforced by static assertion.
- Returns
- reference to the internally stored JSON value if the requested reference type ReferenceType fits to the JSON value; throws type_error.303 otherwise
- Exceptions
-
type_error.303 in case passed type ReferenceType is incompatible with the stored JSON value; see example below
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example shows several calls to get_ref().,get_ref}
- Since
- version 1.1.0
◆ get_ref_impl()
|
inlinestaticprivate |
helper function to implement get_ref()
This function helps to implement get_ref() without code duplication for const and non-const overloads
- Template Parameters
-
ThisType will be deduced as basic_jsonorconst basic_json
- Exceptions
-
type_error.303 if ReferenceType does not match underlying value type of the current JSON
Definition at line 20326 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, altar_valkyrie::obj, and is_valid_types_gen::type.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_to() [1/3]
|
inlinenoexcept |
Definition at line 20682 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::from_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ get_to() [2/3]
|
inline |
◆ get_to() [3/3]
|
inlinenoexcept |
get a value (explicit)
Explicit type conversion between the JSON value and a compatible value. The value is filled into the input parameter by calling the json_serializer<ValueType> from_json() method.
The function is equivalent to executing
This overloads is chosen if:
- ValueType is not basic_json,
- json_serializer<ValueType> has a
from_json()method of the formvoid from_json(const basic_json&, ValueType&), and
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType the input parameter type.
- Returns
- the input parameter, allowing chaining calls.
- Exceptions
-
what json_serializer<ValueType> from_json()method throws
@liveexample{The example below shows several conversions from JSON values to other types. There a few things to note: (1) Floating-point numbers can be converted to integers\, (2) A JSON array can be converted to a standard std::vector<short>\, (3) A JSON object can be converted to C++ associative containers such as std::unordered_map<std::string\, json>.,get_to}
- Since
- version 3.3.0
Definition at line 20658 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::from_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert() [1/6]
|
inline |
inserts elements
Inserts elements from range [first, last).
- Parameters
-
[in] first begin of the range of elements to insert [in] last end of the range of elements to insert
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than objects; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if iterator first or last does does not point to an object; example: "iterators first and last must point to objects"invalid_iterator.210 if first and last do not belong to the same JSON value; example: "iterators do not fit"
@complexity Logarithmic: O(N*log(size() + N)), where N is the number of elements to insert.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert__range_object}
- Since
- version 3.0.0
Definition at line 23314 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, nlohmann::detail::iter_impl< BasicJsonType >::m_it, m_value, nlohmann::detail::internal_iterator< BasicJsonType >::object_iterator, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert() [2/6]
|
inline |
inserts element
inserts element Inserts element val before iterator pos.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator before which the content will be inserted; may be the end() iterator [in] val element to insert
- Returns
- iterator pointing to the inserted val.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than arrays; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if pos is not an iterator of *this; example: "iterator does not fit current value"
@complexity Constant plus linear in the distance between pos and end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23143 of file json.hpp.
References insert().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert() [3/6]
|
inline |
inserts element
Inserts element val before iterator pos.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator before which the content will be inserted; may be the end() iterator [in] val element to insert
- Returns
- iterator pointing to the inserted val.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than arrays; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if pos is not an iterator of *this; example: "iterator does not fit current value"
@complexity Constant plus linear in the distance between pos and end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23121 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), insert_iterator(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, and type_name().
Referenced by insert().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ insert() [4/6]
|
inline |
inserts elements
Inserts elements from range [first, last) before iterator pos.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator before which the content will be inserted; may be the end() iterator [in] first begin of the range of elements to insert [in] last end of the range of elements to insert
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than arrays; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if pos is not an iterator of *this; example: "iterator does not fit current value"invalid_iterator.210 if first and last do not belong to the same JSON value; example: "iterators do not fit"invalid_iterator.211 if first or last are iterators into container for which insert is called; example: "passed iterators may not belong to container"
- Returns
- iterator pointing to the first element inserted, or pos if
first==last
@complexity Linear in std::distance(first, last) plus linear in the distance between pos and end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert__range}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23220 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::internal_iterator< BasicJsonType >::array_iterator, nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), insert_iterator(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, nlohmann::detail::iter_impl< BasicJsonType >::m_it, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert() [5/6]
|
inline |
inserts elements
Inserts elements from initializer list ilist before iterator pos.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator before which the content will be inserted; may be the end() iterator [in] ilist initializer list to insert the values from
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than arrays; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if pos is not an iterator of *this; example: "iterator does not fit current value"
- Returns
- iterator pointing to the first element inserted, or pos if
ilistis empty
@complexity Linear in ilist.size() plus linear in the distance between pos and end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert__ilist}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23273 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), insert_iterator(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert() [6/6]
|
inline |
inserts elements
Inserts cnt copies of val before iterator pos.
- Parameters
-
[in] pos iterator before which the content will be inserted; may be the end() iterator [in] cnt number of copies of val to insert [in] val element to insert
- Returns
- iterator pointing to the first element inserted, or pos if
cnt==0
- Exceptions
-
type_error.309 if called on JSON values other than arrays; example: "cannot use insert() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if pos is not an iterator of *this; example: "iterator does not fit current value"
@complexity Linear in cnt plus linear in the distance between pos and end of the container.
@liveexample{The example shows how insert() is used.,insert__count}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23172 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), insert_iterator(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ insert_iterator()
|
inline |
Helper for insertion of an iterator
- Note
- : This uses std::distance to support GCC 4.8, see https://github.com/nlohmann/json/pull/1257
Definition at line 23082 of file json.hpp.
References make_face_from_files::args, nlohmann::detail::internal_iterator< BasicJsonType >::array_iterator, JSON_ASSERT, nlohmann::detail::iter_impl< BasicJsonType >::m_it, m_value, rotate-tower::result, and set_parents().
Referenced by insert().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_array()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is an array
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is an array.
- Returns
trueif type is array,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_array() for all JSON types.,is_array}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20098 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array.
Referenced by at(), emplace_back(), erase(), get_impl_ptr(), insert(), is_structured(), operator[](), push_back(), and swap().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_binary()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is a binary array
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a binary array.
- Returns
trueif type is binary array,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_binary() for all JSON types.,is_binary}
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 20142 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::binary.
Referenced by erase(), get_binary(), get_impl_ptr(), is_primitive(), and swap().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_boolean()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is a boolean
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a boolean.
- Returns
trueif type is boolean,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_boolean() for all JSON types.,is_boolean}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19939 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::boolean.
Referenced by get_impl(), get_impl_ptr(), and is_primitive().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_discarded()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is discarded
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value was discarded during parsing with a callback function (see parser_callback_t).
- Note
- This function will always be
falsefor JSON values after parsing. That is, discarded values can only occur during parsing, but will be removed when inside a structured value or replaced by null in other cases.
- Returns
trueif type is discarded,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_discarded() for all JSON types.,is_discarded}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20169 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::discarded.
◆ is_null()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is null
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is null.
- Returns
trueif type is null,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_null() for all JSON types.,is_null}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19917 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::null.
Referenced by emplace(), emplace_back(), is_primitive(), operator[](), push_back(), and update().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_number()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is a number
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a number. This includes both integer (signed and unsigned) and floating-point values.
- Returns
trueif type is number (regardless whether integer, unsigned integer or floating-type),falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_number() for all JSON types.,is_number}
- See also
- see is_number_integer() – check if value is an integer or unsigned integer number
- see is_number_unsigned() – check if value is an unsigned integer number
- see is_number_float() – check if value is a floating-point number
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19969 of file json.hpp.
References is_number_float(), and is_number_integer().
Referenced by is_primitive().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_number_float()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is a floating-point number
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a floating-point number. This excludes signed and unsigned integer values.
- Returns
trueif type is a floating-point number,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_number_float() for all JSON types.,is_number_float}
- See also
- see is_number() – check if value is number
- see is_number_integer() – check if value is an integer number
- see is_number_unsigned() – check if value is an unsigned integer number
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20054 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::number_float.
Referenced by get_impl_ptr(), and is_number().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_number_integer()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is an integer number
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a signed or unsigned integer number. This excludes floating-point values.
- Returns
trueif type is an integer or unsigned integer number,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_number_integer() for all JSON types.,is_number_integer}
- See also
- see is_number() – check if value is a number
- see is_number_unsigned() – check if value is an unsigned integer number
- see is_number_float() – check if value is a floating-point number
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19998 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::number_integer, and nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned.
Referenced by get_impl_ptr(), and is_number().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_number_unsigned()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is an unsigned integer number
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is an unsigned integer number. This excludes floating-point and signed integer values.
- Returns
trueif type is an unsigned integer number,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_number_unsigned() for all JSON types.,is_number_unsigned}
- See also
- see is_number() – check if value is a number
- see is_number_integer() – check if value is an integer or unsigned integer number
- see is_number_float() – check if value is a floating-point number
- Since
- version 2.0.0
Definition at line 20026 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned.
Referenced by get_impl_ptr().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_object()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is an object
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is an object.
- Returns
trueif type is object,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_object() for all JSON types.,is_object}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20076 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::object.
Referenced by at(), contains(), count(), emplace(), erase(), find(), get_impl_ptr(), insert(), is_structured(), merge_patch(), operator[](), push_back(), swap(), update(), and value().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_primitive()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether type is primitive
This function returns true if and only if the JSON type is primitive (string, number, boolean, or null).
- Returns
trueif type is primitive (string, number, boolean, or null),falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_primitive() for all JSON types.,is_primitive}
- See also
- see is_structured() – returns whether JSON value is structured
-
see is_null() – returns whether JSON value is
null - see is_string() – returns whether JSON value is a string
- see is_boolean() – returns whether JSON value is a boolean
- see is_number() – returns whether JSON value is a number
- see is_binary() – returns whether JSON value is a binary array
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19868 of file json.hpp.
References is_binary(), is_boolean(), is_null(), is_number(), and is_string().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ is_string()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether value is a string
This function returns true if and only if the JSON value is a string.
- Returns
trueif type is string,falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_string() for all JSON types.,is_string}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 20120 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by erase(), get_impl_ptr(), is_primitive(), and swap().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ is_structured()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return whether type is structured
This function returns true if and only if the JSON type is structured (array or object).
- Returns
trueif type is structured (array or object),falseotherwise.
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies is_structured() for all JSON types.,is_structured}
- See also
- see is_primitive() – returns whether value is primitive
- see is_array() – returns whether value is an array
- see is_object() – returns whether value is an object
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19895 of file json.hpp.
References is_array(), and is_object().
Referenced by assert_invariant().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ items() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
helper to access iterator member functions in range-based for
This function allows to access iterator::key() and iterator::value() during range-based for loops. In these loops, a reference to the JSON values is returned, so there is no access to the underlying iterator.
For loop without items() function:
Range-based for loop without items() function:
Range-based for loop with items() function:
The items() function also allows to use structured bindings (C++17):
- Note
- When iterating over an array,
key()will return the index of the element as string (see example). For primitive types (e.g., numbers),key()returns an empty string.
- Warning
- Using
items()on temporary objects is dangerous. Make sure the object's lifetime exeeds the iteration. See https://github.com/nlohmann/json/issues/2040 for more information.
- Returns
- iteration proxy object wrapping ref with an interface to use in range-based for loops
@liveexample{The following code shows how the function is used.,items}
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 3.1.0, structured bindings support since 3.5.0.
◆ items() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
helper to access iterator member functions in range-based for
This function allows to access iterator::key() and iterator::value() during range-based for loops. In these loops, a reference to the JSON values is returned, so there is no access to the underlying iterator.
For loop without items() function:
Range-based for loop without items() function:
Range-based for loop with items() function:
The items() function also allows to use structured bindings (C++17):
- Note
- When iterating over an array,
key()will return the index of the element as string (see example). For primitive types (e.g., numbers),key()returns an empty string.
- Warning
- Using
items()on temporary objects is dangerous. Make sure the object's lifetime exeeds the iteration. See https://github.com/nlohmann/json/issues/2040 for more information.
- Returns
- iteration proxy object wrapping ref with an interface to use in range-based for loops
@liveexample{The following code shows how the function is used.,items}
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- version 3.1.0, structured bindings support since 3.5.0.
◆ iterator_wrapper() [1/2]
|
inlinestaticnoexcept |
wrapper to access iterator member functions in range-based for
This function allows to access iterator::key() and iterator::value() during range-based for loops. In these loops, a reference to the JSON values is returned, so there is no access to the underlying iterator.
For loop without iterator_wrapper:
Range-based for loop without iterator proxy:
Range-based for loop with iterator proxy:
- Note
- When iterating over an array,
key()will return the index of the element as string (see example).
- Parameters
-
[in] ref reference to a JSON value
- Returns
- iteration proxy object wrapping ref with an interface to use in range-based for loops
@liveexample{The following code shows how the wrapper is used,iterator_wrapper}
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Note
- The name of this function is not yet final and may change in the future.
- Deprecated:
- This stream operator is deprecated and will be removed in future 4.0.0 of the library. Please use items() instead; that is, replace
json::iterator_wrapper(j)withj.items().
◆ iterator_wrapper() [2/2]
|
inlinestaticnoexcept |
wrapper to access iterator member functions in range-based for
This function allows to access iterator::key() and iterator::value() during range-based for loops. In these loops, a reference to the JSON values is returned, so there is no access to the underlying iterator.
For loop without iterator_wrapper:
Range-based for loop without iterator proxy:
Range-based for loop with iterator proxy:
- Note
- When iterating over an array,
key()will return the index of the element as string (see example).
- Parameters
-
[in] ref reference to a JSON value
- Returns
- iteration proxy object wrapping ref with an interface to use in range-based for loops
@liveexample{The following code shows how the wrapper is used,iterator_wrapper}
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes in the JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Note
- The name of this function is not yet final and may change in the future.
- Deprecated:
- This stream operator is deprecated and will be removed in future 4.0.0 of the library. Please use items() instead; that is, replace
json::iterator_wrapper(j)withj.items().
◆ json_value() [1/16]
|
privatedefault |
default constructor (for null values)
◆ json_value() [2/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [3/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [4/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ json_value() [5/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [6/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [7/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [8/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [9/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [10/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ json_value() [11/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ json_value() [12/16]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ json_value() [13/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [14/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [15/16]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ json_value() [16/16]
|
inlineprivate |
constructor for empty values of a given type
Definition at line 18385 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, array, basic_json(), nlohmann::detail::binary, binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::other_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, nlohmann::detail::string, and Floor::t.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ max_size()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns the maximum possible number of elements
Returns the maximum number of elements a JSON value is able to hold due to system or library implementation limitations, i.e. std::distance(begin(), end()) for the JSON value.
- Returns
- The return value depends on the different types and is defined as follows:
Value type return value null 0(same assize())boolean 1(same assize())string 1(same assize())number 1(same assize())binary 1(same assize())object result of function object_t::max_size()array result of function array_t::max_size()
@liveexample{The following code calls max_size() on the different value types. Note the output is implementation specific.,max_size}
@complexity Constant, as long as array_t and object_t satisfy the Container concept; that is, their max_size() functions have constant complexity.
@iterators No changes.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of returning
b.size()wherebis the largest possible JSON value.
- See also
- see size() – returns the number of elements
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22649 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, size(), and nlohmann::detail::string.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ merge_patch()
|
inline |
applies a JSON Merge Patch
The merge patch format is primarily intended for use with the HTTP PATCH method as a means of describing a set of modifications to a target resource's content. This function applies a merge patch to the current JSON value.
The function implements the following algorithm from Section 2 of RFC 7396 (JSON Merge Patch):
Thereby, Target is the current object; that is, the patch is applied to the current value.
- Parameters
-
[in] apply_patch the patch to apply
@complexity Linear in the lengths of patch.
@liveexample{The following code shows how a JSON Merge Patch is applied to a JSON document.,merge_patch}
- See also
- see patch – apply a JSON patch
- RFC 7396 (JSON Merge Patch)
- Since
- version 3.0.0
Definition at line 26280 of file json.hpp.
References erase(), is_object(), merge_patch(), object(), and operator[]().
Referenced by merge_patch().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ meta()
|
inlinestatic |
returns version information on the library
This function returns a JSON object with information about the library, including the version number and information on the platform and compiler.
- Returns
- JSON object holding version information
key description compilerInformation on the used compiler. It is an object with the following keys: c++(the used C++ standard),family(the compiler family; possible values areclang,icc,gcc,ilecpp,msvc,pgcpp,sunpro, andunknown), andversion(the compiler version).copyrightThe copyright line for the library as string. nameThe name of the library as string. platformThe used platform as string. Possible values are win32,linux,apple,unix, andunknown.urlThe URL of the project as string. versionThe version of the library. It is an object with the following keys: major,minor, andpatchas defined by Semantic Versioning, andstring(the version string).
@liveexample{The following code shows an example output of the meta() function.,meta}
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@complexity Constant.
- Since
- 2.1.0
Definition at line 17735 of file json.hpp.
References NLOHMANN_JSON_VERSION_MAJOR, NLOHMANN_JSON_VERSION_MINOR, NLOHMANN_JSON_VERSION_PATCH, rotate-tower::result, and nlohmann::to_string().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ object()
|
inlinestatic |
explicitly create an object from an initializer list
Creates a JSON object value from a given initializer list. The initializer lists elements must be pairs, and their first elements must be strings. If the initializer list is empty, the empty object {} is created.
- Note
- This function is only added for symmetry reasons. In contrast to the related function array(initializer_list_t), there are no cases which can only be expressed by this function. That is, any initializer list init can also be passed to the initializer list constructor basic_json(initializer_list_t, bool, value_t).
- Parameters
-
[in] init initializer list to create an object from (optional)
- Returns
- JSON object value
- Exceptions
-
type_error.301 if init is not a list of pairs whose first elements are strings. In this case, no object can be created. When such a value is passed to basic_json(initializer_list_t, bool, value_t), an array would have been created from the passed initializer list init. See example below.
@complexity Linear in the size of init.
@exceptionsafety Strong guarantee: if an exception is thrown, there are no changes to any JSON value.
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for the object function.,object}
- See also
- see basic_json(initializer_list_t, bool, value_t) – create a JSON value from an initializer list
- see array(initializer_list_t) – create a JSON array value from an initializer list
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19326 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by diff(), and merge_patch().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ operator value_t()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return the type of the JSON value (implicit)
Implicitly return the type of the JSON value as a value from the value_t enumeration.
- Returns
- the type of the JSON value
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies the value_t operator for all JSON types.,operator__value_t}
- See also
- see type() – return the type of the JSON value (explicit)
- see type_name() – return the type as string
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator ValueType()
|
inline |
get a value (implicit)
Implicit type conversion between the JSON value and a compatible value. The call is realized by calling get() const.
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType non-pointer type compatible to the JSON value, for instance intfor JSON integer numbers,boolfor JSON booleans, orstd::vectortypes for JSON arrays. The character type of string_t as well as an initializer list of this type is excluded to avoid ambiguities as these types implicitly convert tostd::string.
- Returns
- copy of the JSON value, converted to type ValueType
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 in case passed type ValueType is incompatible to the JSON value type (e.g., the JSON value is of type boolean, but a string is requested); see example below
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value.
@liveexample{The example below shows several conversions from JSON values to other types. There a few things to note: (1) Floating-point numbers can be converted to integers\, (2) A JSON array can be converted to a standard std::vector<short>\, (3) A JSON object can be converted to C++ associative containers such as std::unordered_map<std::string\, json>.,operator__ValueType}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator+=() [1/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an array
add an object to an array Appends the given element val to the end of the JSON value. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty array is created before appending val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON array
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON array or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Amortized constant.
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON array. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON array.,push_back}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22834 of file json.hpp.
References push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator+=() [2/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an array
add an object to an array Appends the given element val to the end of the JSON value. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty array is created before appending val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON array
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON array or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Amortized constant.
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON array. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON array.,push_back}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22870 of file json.hpp.
References push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator+=() [3/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an object
add an object to an object Inserts the given element val to the JSON object. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty object is created before inserting val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON object
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON object or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container, O(log(size())).
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON object. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON object.,push_back__object_t__value}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22921 of file json.hpp.
References push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator+=() [4/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an object
add an object to an object This function allows to use push_back with an initializer list. In case
- the current value is an object,
- the initializer list init contains only two elements, and
- the first element of init is a string,
init is converted into an object element and added using push_back(const typename object_t::value_type&). Otherwise, init is converted to a JSON value and added using push_back(basic_json&&).
- Parameters
-
[in] init an initializer list
@complexity Linear in the size of the initializer list init.
- Note
- This function is required to resolve an ambiguous overload error, because pairs like
{"key", "value"}can be both interpreted asobject_t::value_typeorstd::initializer_list<basic_json>, see https://github.com/nlohmann/json/issues/235 for more information.
@liveexample{The example shows how initializer lists are treated as objects when possible.,push_back__initializer_list}
Definition at line 22970 of file json.hpp.
References init(), and push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator=()
|
inlinenoexcept |
copy assignment
Copy assignment operator. Copies a JSON value via the "copy and swap" strategy: It is expressed in terms of the copy constructor, destructor, and the swap() member function.
- Parameters
-
[in] other value to copy from
@complexity Linear.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- The complexity is linear.
@liveexample{The code below shows and example for the copy assignment. It creates a copy of value a which is then swapped with b. Finally\, the copy of a (which is the null value after the swap) is destroyed.,basic_json__copyassignment}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19686 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), m_value, set_parents(), and swap().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [1/8]
|
inline |
access specified element via JSON Pointer
Uses a JSON pointer to retrieve a reference to the respective JSON value. No bound checking is performed. Similar to operator[](const typename object_t::key_type&), null values are created in arrays and objects if necessary.
In particular:
- If the JSON pointer points to an object key that does not exist, it is created an filled with a
nullvalue before a reference to it is returned. - If the JSON pointer points to an array index that does not exist, it is created an filled with a
nullvalue before a reference to it is returned. All indices between the current maximum and the given index are also filled withnull. - The special value
-is treated as a synonym for the index past the end.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr a JSON pointer
- Returns
- reference to the element pointed to by ptr
@complexity Constant.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.106 if an array index begins with '0' parse_error.109 if an array index was not a number out_of_range.404 if the JSON pointer can not be resolved
@liveexample{The behavior is shown in the example.,operatorjson_pointer}
- Since
- version 2.0.0
◆ operator[]() [2/8]
|
inline |
access specified element via JSON Pointer
Uses a JSON pointer to retrieve a reference to the respective JSON value. No bound checking is performed. The function does not change the JSON value; no null values are created. In particular, the special value - yields an exception.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr JSON pointer to the desired element
- Returns
- const reference to the element pointed to by ptr
@complexity Constant.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.106 if an array index begins with '0' parse_error.109 if an array index was not a number out_of_range.402 if the array index '-' is used out_of_range.404 if the JSON pointer can not be resolved
@liveexample{The behavior is shown in the example.,operatorjson_pointer_const}
- Since
- version 2.0.0
◆ operator[]() [3/8]
|
inline |
access specified object element
Returns a reference to the element at with specified key key.
- Note
- If key is not found in the object, then it is silently added to the object and filled with a
nullvalue to makekeya valid reference. In case the value wasnullbefore, it is converted to an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- reference to the element at key key
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an object or null; in that cases, using the [] operator with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read and written using the [] operator.,operatorarray__key_type}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21138 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [4/8]
|
inline |
read-only access specified object element
Returns a const reference to the element at with specified key key. No bounds checking is performed.
- Warning
- If the element with key key does not exist, the behavior is undefined.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- const reference to the element at key key
- Precondition
- The element with key key must exist. This precondition is enforced with an assertion.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an object; in that case, using the [] operator with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read using the [] operator.,operatorarray__key_type_const}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21187 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_ASSERT, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [5/8]
access specified array element
Returns a reference to the element at specified location idx.
- Note
- If idx is beyond the range of the array (i.e.,
idx >= size()), then the array is silently filled up withnullvalues to makeidxa valid reference to the last stored element.
- Parameters
-
[in] idx index of the element to access
- Returns
- reference to the element at index idx
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an array or null; in that cases, using the [] operator with an index makes no sense.
@complexity Constant if idx is in the range of the array. Otherwise linear in idx - size().
@liveexample{The example below shows how array elements can be read and written using [] operator. Note the addition of null values.,operatorarray__size_type}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21047 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), begin(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), is_null(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, set_parents(), and type_name().
Referenced by merge_patch().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [6/8]
|
inline |
access specified array element
Returns a const reference to the element at specified location idx.
- Parameters
-
[in] idx index of the element to access
- Returns
- const reference to the element at index idx
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an array; in that case, using the [] operator with an index makes no sense.
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how array elements can be read using the [] operator.,operatorarray__size_type_const}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21100 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [7/8]
|
inline |
access specified object element
Returns a reference to the element at with specified key key.
- Note
- If key is not found in the object, then it is silently added to the object and filled with a
nullvalue to makekeya valid reference. In case the value wasnullbefore, it is converted to an object.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- reference to the element at key key
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an object or null; in that cases, using the [] operator with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read and written using the [] operator.,operatorarray__key_type}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.1.0
Definition at line 21228 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ operator[]() [8/8]
|
inline |
read-only access specified object element
Returns a const reference to the element at with specified key key. No bounds checking is performed.
- Warning
- If the element with key key does not exist, the behavior is undefined.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access
- Returns
- const reference to the element at key key
- Precondition
- The element with key key must exist. This precondition is enforced with an assertion.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.305 if the JSON value is not an object; in that case, using the [] operator with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be read using the [] operator.,operatorarray__key_type_const}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see value() for access by value with a default value
- Since
- version 1.1.0
Definition at line 21279 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_ASSERT, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ parse() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24298 of file json.hpp.
References parser(), and rotate-tower::result.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ parse() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
deserialize from a compatible input
- Template Parameters
-
InputType A compatible input, for instance - an std::istream object
- a FILE pointer
- a C-style array of characters
- a pointer to a null-terminated string of single byte characters
- an object obj for which begin(obj) and end(obj) produces a valid pair of iterators.
- Parameters
-
[in] i input to read from [in] cb a parser callback function of type parser_callback_t which is used to control the deserialization by filtering unwanted values (optional) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default) [in] ignore_comments whether comments should be ignored and treated like whitespace (true) or yield a parse error (true); (optional, false by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.101 if a parse error occurs; example: ""unexpected end of input; expected string literal""parse_error.102 if to_unicode fails or surrogate error parse_error.103 if to_unicode fails
@complexity Linear in the length of the input. The parser is a predictive LL(1) parser. The complexity can be higher if the parser callback function cb or reading from the input i has a super-linear complexity.
- Note
- A UTF-8 byte order mark is silently ignored.
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the parse() function reading from an array.,parse__array__parser_callback_t}
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the parse() function with and without callback function.,parse__string__parser_callback_t}
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the parse() function with and without callback function.,parse__istream__parser_callback_t}
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the parse() function reading from a contiguous container.,parse__contiguouscontainer__parser_callback_t}
- Since
- version 2.0.3 (contiguous containers); version 3.9.0 allowed to ignore comments.
Definition at line 24247 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), parser(), and rotate-tower::result.
Referenced by operator""_json().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ parse() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
deserialize from a pair of character iterators
The value_type of the iterator must be a integral type with size of 1, 2 or 4 bytes, which will be interpreted respectively as UTF-8, UTF-16 and UTF-32.
- Parameters
-
[in] first iterator to start of character range [in] last iterator to end of character range [in] cb a parser callback function of type parser_callback_t which is used to control the deserialization by filtering unwanted values (optional) [in] allow_exceptions whether to throw exceptions in case of a parse error (optional, true by default) [in] ignore_comments whether comments should be ignored and treated like whitespace (true) or yield a parse error (true); (optional, false by default)
- Returns
- deserialized JSON value; in case of a parse error and allow_exceptions set to
false, the return value will be value_t::discarded.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.101 if a parse error occurs; example: ""unexpected end of input; expected string literal""parse_error.102 if to_unicode fails or surrogate error parse_error.103 if to_unicode fails
Definition at line 24285 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), parser(), and rotate-tower::result.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ parser()
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 17586 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by accept(), parse(), and sax_parse().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ patch()
|
inline |
applies a JSON patch
JSON Patch defines a JSON document structure for expressing a sequence of operations to apply to a JSON) document. With this function, a JSON Patch is applied to the current JSON value by executing all operations from the patch.
- Parameters
-
[in] json_patch JSON patch document
- Returns
- patched document
- Note
- The application of a patch is atomic: Either all operations succeed and the patched document is returned or an exception is thrown. In any case, the original value is not changed: the patch is applied to a copy of the value.
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.104 if the JSON patch does not consist of an array of objects parse_error.105 if the JSON patch is malformed (e.g., mandatory attributes are missing); example: "operation add must have member path"out_of_range.401 if an array index is out of range. out_of_range.403 if a JSON pointer inside the patch could not be resolved successfully in the current JSON value; example: "key baz not found"out_of_range.405 if JSON pointer has no parent ("add", "remove", "move") other_error.501 if "test" operation was unsuccessful
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value and the length of the JSON patch. As usually only a fraction of the JSON value is affected by the patch, the complexity can usually be neglected.
@liveexample{The following code shows how a JSON patch is applied to a value.,patch}
- See also
- see diff – create a JSON patch by comparing two JSON values
- RFC 6902 (JSON Patch)
- RFC 6901 (JSON Pointer)
- Since
- version 2.0.0
Definition at line 25791 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::json_pointer< BasicJsonType >::array_index(), nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::parse_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::out_of_range::create(), nlohmann::detail::other_error::create(), nlohmann::detail::discarded, JSON_ASSERT, JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_INTERNAL_CATCH, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, give::op, python_init::path, replace(), rotate-tower::result, nlohmann::detail::string, and nlohmann::to_string().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ push_back() [1/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an array
Appends the given element val to the end of the JSON value. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty array is created before appending val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON array
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON array or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Amortized constant.
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON array. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON array.,push_back}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22807 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), is_null(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, set_parent(), and type_name().
Referenced by create_map_in_quest_array(), create_region_array(), fill_json(), operator+=(), and push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ push_back() [2/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an array
add an object to an array Appends the given element val to the end of the JSON value. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty array is created before appending val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON array
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON array or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Amortized constant.
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON array. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON array.,push_back}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22844 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), is_null(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ push_back() [3/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an object
Inserts the given element val to the JSON object. If the function is called on a JSON null value, an empty object is created before inserting val.
- Parameters
-
[in] val the value to add to the JSON object
- Exceptions
-
type_error.308 when called on a type other than JSON object or null; example: "cannot use push_back() with number"
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container, O(log(size())).
@liveexample{The example shows how push_back() and += can be used to add elements to a JSON object. Note how the null value was silently converted to a JSON object.,push_back__object_t__value}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22896 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, altar_valkyrie::res, set_parent(), and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ push_back() [4/4]
|
inline |
add an object to an object
This function allows to use push_back with an initializer list. In case
- the current value is an object,
- the initializer list init contains only two elements, and
- the first element of init is a string,
init is converted into an object element and added using push_back(const typename object_t::value_type&). Otherwise, init is converted to a JSON value and added using push_back(basic_json&&).
- Parameters
-
[in] init an initializer list
@complexity Linear in the size of the initializer list init.
- Note
- This function is required to resolve an ambiguous overload error, because pairs like
{"key", "value"}can be both interpreted asobject_t::value_typeorstd::initializer_list<basic_json>, see https://github.com/nlohmann/json/issues/235 for more information.
@liveexample{The example shows how initializer lists are treated as objects when possible.,push_back__initializer_list}
Definition at line 22952 of file json.hpp.
References basic_json(), init(), is_object(), and push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ rbegin() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const reverse iterator to the last element
Returns a const iterator to the reverse-beginning; that is, the last element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).rbegin().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for crbegin().,crbegin}
- See also
- see rbegin() – returns a reverse iterator to the beginning
- see rend() – returns a reverse iterator to the end
- see crend() – returns a const reverse iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22185 of file json.hpp.
References crbegin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ rbegin() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns an iterator to the reverse-beginning
Returns an iterator to the reverse-beginning; that is, the last element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
reverse_iterator(end()).
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for rbegin().,rbegin}
- See also
- see crbegin() – returns a const reverse iterator to the beginning
- see rend() – returns a reverse iterator to the end
- see crend() – returns a const reverse iterator to the end
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22177 of file json.hpp.
References end().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ rend() [1/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns a const reverse iterator to one before the first
Returns a const reverse iterator to the reverse-end; that is, one before the first element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
const_cast<const basic_json&>(*this).rend().
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for crend().,crend}
- See also
- see rend() – returns a reverse iterator to the end
- see rbegin() – returns a reverse iterator to the beginning
- see crbegin() – returns a const reverse iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22222 of file json.hpp.
References crend().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ rend() [2/2]
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns an iterator to the reverse-end
Returns an iterator to the reverse-end; that is, one before the first element.
@complexity Constant.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the ReversibleContainer requirements:
- The complexity is constant.
- Has the semantics of
reverse_iterator(begin()).
@liveexample{The following code shows an example for rend().,rend}
- See also
- see crend() – returns a const reverse iterator to the end
- see rbegin() – returns a reverse iterator to the beginning
- see crbegin() – returns a const reverse iterator to the beginning
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22214 of file json.hpp.
References begin().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ sax_parse() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24429 of file json.hpp.
References parser(), and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ sax_parse() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
generate SAX events
The SAX event lister must follow the interface of json_sax.
This function reads from a compatible input. Examples are:
- an std::istream object
- a FILE pointer
- a C-style array of characters
- a pointer to a null-terminated string of single byte characters
- an object obj for which begin(obj) and end(obj) produces a valid pair of iterators.
- Parameters
-
[in] i input to read from [in,out] sax SAX event listener [in] format the format to parse (JSON, CBOR, MessagePack, or UBJSON) [in] strict whether the input has to be consumed completely [in] ignore_comments whether comments should be ignored and treated like whitespace (true) or yield a parse error (true); (optional, false by default); only applies to the JSON file format.
- Returns
- return value of the last processed SAX event
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.101 if a parse error occurs; example: ""unexpected end of input; expected string literal""parse_error.102 if to_unicode fails or surrogate error parse_error.103 if to_unicode fails
@complexity Linear in the length of the input. The parser is a predictive LL(1) parser. The complexity can be higher if the SAX consumer sax has a super-linear complexity.
- Note
- A UTF-8 byte order mark is silently ignored.
@liveexample{The example below demonstrates the sax_parse() function reading from string and processing the events with a user-defined SAX event consumer.,sax_parse}
- Since
- version 3.2.0
Definition at line 24402 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), parser(), and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ sax_parse() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24415 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::input_adapter(), parser(), and nlohmann::detail::binary_reader< BasicJsonType, InputAdapterType, SAX >::sax_parse().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ set_parent()
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 18705 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, JSON_ASSERT, JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, m_value, set_parents(), and type().
Referenced by at(), emplace(), emplace_back(), operator[](), and push_back().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ set_parents() [1/2]
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 18655 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, board::element, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by basic_json(), insert_iterator(), operator=(), operator[](), set_parent(), and swap().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ set_parents() [2/2]
|
inlineprivate |
◆ size()
|
inlinenoexcept |
returns the number of elements
Returns the number of elements in a JSON value.
- Returns
- The return value depends on the different types and is defined as follows:
Value type return value null 0boolean 1string 1number 1binary 1object result of function object_t::size() array result of function array_t::size()
@liveexample{The following code calls size() on the different value types.,size}
@complexity Constant, as long as array_t and object_t satisfy the Container concept; that is, their size() functions have constant complexity.
@iterators No changes.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
- Note
- This function does not return the length of a string stored as JSON value - it returns the number of elements in the JSON value which is 1 in the case of a string.
@requirement This function helps basic_json satisfying the Container requirements:
- See also
- see empty() – checks whether the container is empty
- see max_size() – returns the maximal number of elements
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 22571 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, m_value, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by erase(), and max_size().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ swap() [1/6]
|
inline |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of a JSON array with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other array to exchange the contents with
- Exceptions
-
type_error.310 when JSON value is not an array; example: "cannot use swap() with string"
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how arrays can be swapped with swap().,swap__array_t}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23521 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_array(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ swap() [2/6]
|
inline |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of a JSON string with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other binary to exchange the contents with
- Exceptions
-
type_error.310 when JSON value is not a string; example: "cannot use swap() with boolean"
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how strings can be swapped with swap().,swap__binary_t}
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 23620 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_binary(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ swap() [3/6]
|
inline |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of a JSON object with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other object to exchange the contents with
- Exceptions
-
type_error.310 when JSON value is not an object; example: "cannot use swap() with string"
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how objects can be swapped with swap().,swap__object_t}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23554 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ swap() [4/6]
|
inlinenoexcept |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of the JSON value with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other JSON value to exchange the contents with
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how JSON values can be swapped with swap().,swap__reference}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23458 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), m_value, and set_parents().
Referenced by operator=().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ swap() [5/6]
|
inline |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of a JSON string with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other string to exchange the contents with
- Exceptions
-
type_error.310 when JSON value is not a string; example: "cannot use swap() with boolean"
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how strings can be swapped with swap().,swap__string_t}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 23587 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_string(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ swap() [6/6]
|
inline |
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of a JSON string with those of other. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] other binary to exchange the contents with
- Exceptions
-
type_error.310 when JSON value is not a string; example: "cannot use swap() with boolean"
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how strings can be swapped with swap().,swap__binary_t}
- Since
- version 3.8.0
Definition at line 23634 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_binary(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_bson() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and returns a vector containing the corresponding BSON-representation.
BSON (Binary JSON) is a binary format in which zero or more ordered key/value pairs are stored as a single entity (a so-called document).
The library uses the following mapping from JSON values types to BSON types:
| JSON value type | value/range | BSON type | marker |
|---|---|---|---|
| null | null | null | 0x0A |
| boolean | true, false | boolean | 0x08 |
| number_integer | -9223372036854775808..-2147483649 | int64 | 0x12 |
| number_integer | -2147483648..2147483647 | int32 | 0x10 |
| number_integer | 2147483648..9223372036854775807 | int64 | 0x12 |
| number_unsigned | 0..2147483647 | int32 | 0x10 |
| number_unsigned | 2147483648..9223372036854775807 | int64 | 0x12 |
| number_unsigned | 9223372036854775808..18446744073709551615 | – | – |
| number_float | any value | double | 0x01 |
| string | any value | string | 0x02 |
| array | any value | document | 0x04 |
| object | any value | document | 0x03 |
| binary | any value | binary | 0x05 |
- Warning
- The mapping is incomplete, since only JSON-objects (and things contained therein) can be serialized to BSON. Also, integers larger than 9223372036854775807 cannot be serialized to BSON, and the keys may not contain U+0000, since they are serialized a zero-terminated c-strings.
- Exceptions
-
out_of_range.407 if j.is_number_unsigned() && j.get<std::uint64_t>() > 9223372036854775807out_of_range.409 if a key in jcontains a NULL (U+0000)type_error.317 if !j.is_object()
- Precondition
- The input
jis required to be an object:j.is_object() == true.
- Parameters
-
[in] j JSON value to serialize
- Returns
- BSON serialization as byte vector
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value j.
@liveexample{The example shows the serialization of a JSON value to a byte vector in BSON format.,to_bson}
- See also
- http://bsonspec.org/spec.html
- see from_bson(detail::input_adapter&&, const bool strict) for the analogous deserialization
- see to_ubjson(const basic_json&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- see to_cbor(const basic_json&) for the related CBOR format
- see to_msgpack(const basic_json&) for the related MessagePack format
Definition at line 24952 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
◆ to_bson() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and forwards the corresponding BSON-representation to the given output_adapter o.
- Parameters
-
j The JSON object to convert to BSON. o The output adapter that receives the binary BSON representation.
- Precondition
- The input
jshall be an object:j.is_object() == true
- See also
- see to_bson(const basic_json&)
Definition at line 24975 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_bson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_bson() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Serializes the given JSON object j to BSON and forwards the corresponding BSON-representation to the given output_adapter o.
- Parameters
-
j The JSON object to convert to BSON. o The output adapter that receives the binary BSON representation.
- Precondition
- The input
jshall be an object:j.is_object() == true
- See also
- see to_bson(const basic_json&)
Definition at line 24967 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_bson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_cbor() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
create a CBOR serialization of a given JSON value
Serializes a given JSON value j to a byte vector using the CBOR (Concise Binary Object Representation) serialization format. CBOR is a binary serialization format which aims to be more compact than JSON itself, yet more efficient to parse.
The library uses the following mapping from JSON values types to CBOR types according to the CBOR specification (RFC 7049):
| JSON value type | value/range | CBOR type | first byte |
|---|---|---|---|
| null | null | Null | 0xF6 |
| boolean | true | True | 0xF5 |
| boolean | false | False | 0xF4 |
| number_integer | -9223372036854775808..-2147483649 | Negative integer (8 bytes follow) | 0x3B |
| number_integer | -2147483648..-32769 | Negative integer (4 bytes follow) | 0x3A |
| number_integer | -32768..-129 | Negative integer (2 bytes follow) | 0x39 |
| number_integer | -128..-25 | Negative integer (1 byte follow) | 0x38 |
| number_integer | -24..-1 | Negative integer | 0x20..0x37 |
| number_integer | 0..23 | Integer | 0x00..0x17 |
| number_integer | 24..255 | Unsigned integer (1 byte follow) | 0x18 |
| number_integer | 256..65535 | Unsigned integer (2 bytes follow) | 0x19 |
| number_integer | 65536..4294967295 | Unsigned integer (4 bytes follow) | 0x1A |
| number_integer | 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | Unsigned integer (8 bytes follow) | 0x1B |
| number_unsigned | 0..23 | Integer | 0x00..0x17 |
| number_unsigned | 24..255 | Unsigned integer (1 byte follow) | 0x18 |
| number_unsigned | 256..65535 | Unsigned integer (2 bytes follow) | 0x19 |
| number_unsigned | 65536..4294967295 | Unsigned integer (4 bytes follow) | 0x1A |
| number_unsigned | 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | Unsigned integer (8 bytes follow) | 0x1B |
| number_float | any value representable by a float | Single-Precision Float | 0xFA |
| number_float | any value NOT representable by a float | Double-Precision Float | 0xFB |
| string | length: 0..23 | UTF-8 string | 0x60..0x77 |
| string | length: 23..255 | UTF-8 string (1 byte follow) | 0x78 |
| string | length: 256..65535 | UTF-8 string (2 bytes follow) | 0x79 |
| string | length: 65536..4294967295 | UTF-8 string (4 bytes follow) | 0x7A |
| string | length: 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | UTF-8 string (8 bytes follow) | 0x7B |
| array | size: 0..23 | array | 0x80..0x97 |
| array | size: 23..255 | array (1 byte follow) | 0x98 |
| array | size: 256..65535 | array (2 bytes follow) | 0x99 |
| array | size: 65536..4294967295 | array (4 bytes follow) | 0x9A |
| array | size: 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | array (8 bytes follow) | 0x9B |
| object | size: 0..23 | map | 0xA0..0xB7 |
| object | size: 23..255 | map (1 byte follow) | 0xB8 |
| object | size: 256..65535 | map (2 bytes follow) | 0xB9 |
| object | size: 65536..4294967295 | map (4 bytes follow) | 0xBA |
| object | size: 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | map (8 bytes follow) | 0xBB |
| binary | size: 0..23 | byte string | 0x40..0x57 |
| binary | size: 23..255 | byte string (1 byte follow) | 0x58 |
| binary | size: 256..65535 | byte string (2 bytes follow) | 0x59 |
| binary | size: 65536..4294967295 | byte string (4 bytes follow) | 0x5A |
| binary | size: 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | byte string (8 bytes follow) | 0x5B |
Binary values with subtype are mapped to tagged values (0xD8..0xDB) depending on the subtype, followed by a byte string, see "binary" cells in the table above.
- Note
- The mapping is complete in the sense that any JSON value type can be converted to a CBOR value.
-
If NaN or Infinity are stored inside a JSON number, they are serialized properly. This behavior differs from the dump() function which serializes NaN or Infinity to
null. -
The following CBOR types are not used in the conversion:
- UTF-8 strings terminated by "break" (0x7F)
- arrays terminated by "break" (0x9F)
- maps terminated by "break" (0xBF)
- byte strings terminated by "break" (0x5F)
- date/time (0xC0..0xC1)
- bignum (0xC2..0xC3)
- decimal fraction (0xC4)
- bigfloat (0xC5)
- expected conversions (0xD5..0xD7)
- simple values (0xE0..0xF3, 0xF8)
- undefined (0xF7)
- half-precision floats (0xF9)
- break (0xFF)
- Parameters
-
[in] j JSON value to serialize
- Returns
- CBOR serialization as byte vector
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value j.
@liveexample{The example shows the serialization of a JSON value to a byte vector in CBOR format.,to_cbor}
- See also
- http://cbor.io
- see from_cbor(InputType&&, const bool, const bool, const cbor_tag_handler_t) for the analogous deserialization
- see to_msgpack(const basic_json&) for the related MessagePack format
- see to_ubjson(const basic_json&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9; compact representation of floating-point numbers since version 3.8.0
Definition at line 24676 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
◆ to_cbor() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24688 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_cbor().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_cbor() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24683 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_cbor().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_msgpack() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
create a MessagePack serialization of a given JSON value
Serializes a given JSON value j to a byte vector using the MessagePack serialization format. MessagePack is a binary serialization format which aims to be more compact than JSON itself, yet more efficient to parse.
The library uses the following mapping from JSON values types to MessagePack types according to the MessagePack specification:
| JSON value type | value/range | MessagePack type | first byte |
|---|---|---|---|
| null | null | nil | 0xC0 |
| boolean | true | true | 0xC3 |
| boolean | false | false | 0xC2 |
| number_integer | -9223372036854775808..-2147483649 | int64 | 0xD3 |
| number_integer | -2147483648..-32769 | int32 | 0xD2 |
| number_integer | -32768..-129 | int16 | 0xD1 |
| number_integer | -128..-33 | int8 | 0xD0 |
| number_integer | -32..-1 | negative fixint | 0xE0..0xFF |
| number_integer | 0..127 | positive fixint | 0x00..0x7F |
| number_integer | 128..255 | uint 8 | 0xCC |
| number_integer | 256..65535 | uint 16 | 0xCD |
| number_integer | 65536..4294967295 | uint 32 | 0xCE |
| number_integer | 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | uint 64 | 0xCF |
| number_unsigned | 0..127 | positive fixint | 0x00..0x7F |
| number_unsigned | 128..255 | uint 8 | 0xCC |
| number_unsigned | 256..65535 | uint 16 | 0xCD |
| number_unsigned | 65536..4294967295 | uint 32 | 0xCE |
| number_unsigned | 4294967296..18446744073709551615 | uint 64 | 0xCF |
| number_float | any value representable by a float | float 32 | 0xCA |
| number_float | any value NOT representable by a float | float 64 | 0xCB |
| string | length: 0..31 | fixstr | 0xA0..0xBF |
| string | length: 32..255 | str 8 | 0xD9 |
| string | length: 256..65535 | str 16 | 0xDA |
| string | length: 65536..4294967295 | str 32 | 0xDB |
| array | size: 0..15 | fixarray | 0x90..0x9F |
| array | size: 16..65535 | array 16 | 0xDC |
| array | size: 65536..4294967295 | array 32 | 0xDD |
| object | size: 0..15 | fix map | 0x80..0x8F |
| object | size: 16..65535 | map 16 | 0xDE |
| object | size: 65536..4294967295 | map 32 | 0xDF |
| binary | size: 0..255 | bin 8 | 0xC4 |
| binary | size: 256..65535 | bin 16 | 0xC5 |
| binary | size: 65536..4294967295 | bin 32 | 0xC6 |
- Note
- The mapping is complete in the sense that any JSON value type can be converted to a MessagePack value.
-
The following values can not be converted to a MessagePack value:
- strings with more than 4294967295 bytes
- byte strings with more than 4294967295 bytes
- arrays with more than 4294967295 elements
- objects with more than 4294967295 elements
- Any MessagePack output created to_msgpack can be successfully parsed by from_msgpack.
-
If NaN or Infinity are stored inside a JSON number, they are serialized properly. This behavior differs from the dump() function which serializes NaN or Infinity to
null.
- Parameters
-
[in] j JSON value to serialize
- Returns
- MessagePack serialization as byte vector
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value j.
@liveexample{The example shows the serialization of a JSON value to a byte vector in MessagePack format.,to_msgpack}
- See also
- http://msgpack.org
- see from_msgpack for the analogous deserialization
- see to_cbor(const basic_json& for the related CBOR format
- see to_ubjson(const basic_json&, const bool, const bool) for the related UBJSON format
- Since
- version 2.0.9
Definition at line 24771 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
◆ to_msgpack() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24783 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_msgpack().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_msgpack() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24778 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_msgpack().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_ubjson() [1/3]
|
inlinestatic |
create a UBJSON serialization of a given JSON value
Serializes a given JSON value j to a byte vector using the UBJSON (Universal Binary JSON) serialization format. UBJSON aims to be more compact than JSON itself, yet more efficient to parse.
The library uses the following mapping from JSON values types to UBJSON types according to the UBJSON specification:
| JSON value type | value/range | UBJSON type | marker |
|---|---|---|---|
| null | null | null | Z |
| boolean | true | true | T |
| boolean | false | false | F |
| number_integer | -9223372036854775808..-2147483649 | int64 | L |
| number_integer | -2147483648..-32769 | int32 | l |
| number_integer | -32768..-129 | int16 | I |
| number_integer | -128..127 | int8 | i |
| number_integer | 128..255 | uint8 | U |
| number_integer | 256..32767 | int16 | I |
| number_integer | 32768..2147483647 | int32 | l |
| number_integer | 2147483648..9223372036854775807 | int64 | L |
| number_unsigned | 0..127 | int8 | i |
| number_unsigned | 128..255 | uint8 | U |
| number_unsigned | 256..32767 | int16 | I |
| number_unsigned | 32768..2147483647 | int32 | l |
| number_unsigned | 2147483648..9223372036854775807 | int64 | L |
| number_unsigned | 2147483649..18446744073709551615 | high-precision | H |
| number_float | any value | float64 | D |
| string | with shortest length indicator | string | S |
| array | see notes on optimized format | array | [ |
| object | see notes on optimized format | map | { |
- Note
- The mapping is complete in the sense that any JSON value type can be converted to a UBJSON value.
-
The following values can not be converted to a UBJSON value:
- strings with more than 9223372036854775807 bytes (theoretical)
-
The following markers are not used in the conversion:
Z: no-op values are not created.C: single-byte strings are serialized withSmarkers.
- Any UBJSON output created to_ubjson can be successfully parsed by from_ubjson.
-
If NaN or Infinity are stored inside a JSON number, they are serialized properly. This behavior differs from the dump() function which serializes NaN or Infinity to
null. - The optimized formats for containers are supported: Parameter use_size adds size information to the beginning of a container and removes the closing marker. Parameter use_type further checks whether all elements of a container have the same type and adds the type marker to the beginning of the container. The use_type parameter must only be used together with use_size = true. Note that use_size = true alone may result in larger representations - the benefit of this parameter is that the receiving side is immediately informed on the number of elements of the container.
- If the JSON data contains the binary type, the value stored is a list of integers, as suggested by the UBJSON documentation. In particular, this means that serialization and the deserialization of a JSON containing binary values into UBJSON and back will result in a different JSON object.
- Parameters
-
[in] j JSON value to serialize [in] use_size whether to add size annotations to container types [in] use_type whether to add type annotations to container types (must be combined with use_size = true)
- Returns
- UBJSON serialization as byte vector
@complexity Linear in the size of the JSON value j.
@liveexample{The example shows the serialization of a JSON value to a byte vector in UBJSON format.,to_ubjson}
- See also
- http://ubjson.org
- see from_ubjson(InputType&&, const bool, const bool) for the analogous deserialization
- see to_cbor(const basic_json& for the related CBOR format
- see to_msgpack(const basic_json&) for the related MessagePack format
- Since
- version 3.1.0
Definition at line 24874 of file json.hpp.
References rotate-tower::result.
◆ to_ubjson() [2/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24889 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_ubjson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ to_ubjson() [3/3]
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 24883 of file json.hpp.
References disinfect::o, and nlohmann::detail::binary_writer< BasicJsonType, CharType >::write_ubjson().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ type()
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
return the type of the JSON value (explicit)
Return the type of the JSON value as a value from the value_t enumeration.
- Returns
- the type of the JSON value
Value type return value null value_t::null boolean value_t::boolean string value_t::string number (integer) value_t::number_integer number (unsigned integer) value_t::number_unsigned number (floating-point) value_t::number_float object value_t::object array value_t::array binary value_t::binary discarded value_t::discarded
@complexity Constant.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this member function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies type() for all JSON types.,type}
- See also
- see operator value_t() – return the type of the JSON value (implicit)
- see type_name() – return the type as string
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 19837 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by set_parent().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ type_name()
|
inlinenoexcept |
return the type as string
Returns the type name as string to be used in error messages - usually to indicate that a function was called on a wrong JSON type.
- Returns
- a string representation of a the m_type member:
Value type return value null "null"boolean "boolean"string "string"number "number"(for all number types)object "object"array "array"binary "binary"discarded "discarded"
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The following code exemplifies type_name() for all JSON types.,type_name}
- See also
- see type() – return the type of the JSON value
- see operator value_t() – return the type of the JSON value (implicit)
- Since
- version 1.0.0, public since 2.1.0,
const char*andnoexceptsince 3.0.0
Definition at line 24525 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::array, nlohmann::detail::binary, nlohmann::detail::boolean, nlohmann::detail::discarded, nlohmann::detail::null, nlohmann::detail::number_float, nlohmann::detail::number_integer, nlohmann::detail::number_unsigned, nlohmann::detail::object, and nlohmann::detail::string.
Referenced by at(), emplace(), emplace_back(), erase(), get_binary(), get_impl(), insert(), operator[](), push_back(), swap(), update(), and value().
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ unflatten()
|
inline |
unflatten a previously flattened JSON value
The function restores the arbitrary nesting of a JSON value that has been flattened before using the flatten() function. The JSON value must meet certain constraints:
- The value must be an object.
- The keys must be JSON pointers (see RFC 6901)
- The mapped values must be primitive JSON types.
- Returns
- the original JSON from a flattened version
- Note
- Empty objects and arrays are flattened by flatten() to
nullvalues and can not unflattened to their original type. Apart from this example, for a JSON valuej, the following is always true:j == j.flatten().unflatten().
@complexity Linear in the size the JSON value.
- Exceptions
-
type_error.314 if value is not an object type_error.315 if object values are not primitive
@liveexample{The following code shows how a flattened JSON object is unflattened into the original nested JSON object.,unflatten}
- See also
- see flatten() for the reverse function
- Since
- version 2.0.0
Definition at line 25730 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::json_pointer< BasicJsonType >::unflatten().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ update() [1/2]
|
inline |
updates a JSON object from another object, overwriting existing keys
Inserts all values from from range [first, last) and overwrites existing keys.
- Parameters
-
[in] first begin of the range of elements to insert [in] last end of the range of elements to insert
- Exceptions
-
type_error.312 if called on JSON values other than objects; example: "cannot use update() with string"invalid_iterator.202 if iterator first or last does does not point to an object; example: "iterators first and last must point to objects"invalid_iterator.210 if first and last do not belong to the same JSON value; example: "iterators do not fit"
@complexity O(N*log(size() + N)), where N is the number of elements to insert.
@liveexample{The example shows how update() is used__range.,update}
- Since
- version 3.0.0
Definition at line 23407 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), nlohmann::detail::invalid_iterator::create(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ update() [2/2]
|
inline |
updates a JSON object from another object, overwriting existing keys
Inserts all values from JSON object j and overwrites existing keys.
- Parameters
-
[in] j JSON object to read values from
- Exceptions
-
type_error.312 if called on JSON values other than objects; example: "cannot use update() with string"
@complexity O(N*log(size() + N)), where N is the number of elements to insert.
@liveexample{The example shows how update() is used.,update}
- Since
- version 3.0.0
Definition at line 23356 of file json.hpp.
References assert_invariant(), cbegin(), cend(), nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_null(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_UNLIKELY, JSON_THROW, m_value, nlohmann::detail::object, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ value() [1/4]
|
inline |
◆ value() [2/4]
|
inline |
access specified object element via JSON Pointer with default value
Returns either a copy of an object's element at the specified key key or a given default value if no element with key key exists.
The function is basically equivalent to executing
- Note
- Unlike at(const json_pointer&), this function does not throw if the given key key was not found.
- Parameters
-
[in] ptr a JSON pointer to the element to access [in] default_value the value to return if ptr found no value
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType type compatible to JSON values, for instance intfor JSON integer numbers,boolfor JSON booleans, orstd::vectortypes for JSON arrays. Note the type of the expected value at key and the default value default_value must be compatible.
- Returns
- copy of the element at key key or default_value if key is not found
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 if default_value does not match the type of the value at ptr type_error.306 if the JSON value is not an object; in that case, using value()with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be queried with a default value.,basic_json__value_ptr}
- See also
- see operator[](const json_pointer&) for unchecked access by reference
- Since
- version 2.0.2
Definition at line 21417 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_INTERNAL_CATCH, JSON_THROW, JSON_TRY, and type_name().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ value() [3/4]
|
inline |
overload for a default value of type const char*
access specified object element with default value Returns either a copy of an object's element at the specified key key or a given default value if no element with key key exists.
The function is basically equivalent to executing
- Note
- Unlike at(const typename object_t::key_type&), this function does not throw if the given key key was not found.
- Unlike operator[](const typename object_t::key_type& key), this function does not implicitly add an element to the position defined by key. This function is furthermore also applicable to const objects.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access [in] default_value the value to return if key is not found
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType type compatible to JSON values, for instance intfor JSON integer numbers,boolfor JSON booleans, orstd::vectortypes for JSON arrays. Note the type of the expected value at key and the default value default_value must be compatible.
- Returns
- copy of the element at key key or default_value if key is not found
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 if default_value does not match the type of the value at key type_error.306 if the JSON value is not an object; in that case, using value()with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be queried with a default value.,basic_json__value}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see operator[](const typename object_t::key_type&) for unchecked access by reference
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21367 of file json.hpp.
References value().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ value() [4/4]
|
inline |
access specified object element with default value
Returns either a copy of an object's element at the specified key key or a given default value if no element with key key exists.
The function is basically equivalent to executing
- Note
- Unlike at(const typename object_t::key_type&), this function does not throw if the given key key was not found.
- Unlike operator[](const typename object_t::key_type& key), this function does not implicitly add an element to the position defined by key. This function is furthermore also applicable to const objects.
- Parameters
-
[in] key key of the element to access [in] default_value the value to return if key is not found
- Template Parameters
-
ValueType type compatible to JSON values, for instance intfor JSON integer numbers,boolfor JSON booleans, orstd::vectortypes for JSON arrays. Note the type of the expected value at key and the default value default_value must be compatible.
- Returns
- copy of the element at key key or default_value if key is not found
- Exceptions
-
type_error.302 if default_value does not match the type of the value at key type_error.306 if the JSON value is not an object; in that case, using value()with a key makes no sense.
@complexity Logarithmic in the size of the container.
@liveexample{The example below shows how object elements can be queried with a default value.,basic_json__value}
- See also
- see at(const typename object_t::key_type&) for access by reference with range checking
- see operator[](const typename object_t::key_type&) for unchecked access by reference
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Definition at line 21345 of file json.hpp.
References nlohmann::detail::type_error::create(), end(), find(), is_object(), JSON_HEDLEY_LIKELY, JSON_THROW, and type_name().
Referenced by json_value(), value(), and inja::Renderer::visit().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Friends And Related Function Documentation
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::binary_reader
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::binary_writer
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::exception
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::iter_impl
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::json_sax_dom_callback_parser
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::json_sax_dom_parser
|
friend |
◆ ::nlohmann::detail::parser
|
friend |
◆ detail::external_constructor
|
friend |
◆ operator!= [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: not equal
Compares two JSON values for inequality by calculating not (lhs == rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are not equal
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__notequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator!= [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: not equal
comparison: not equal Compares two JSON values for inequality by calculating not (lhs == rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are not equal
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__notequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator!= [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: not equal
comparison: not equal Compares two JSON values for inequality by calculating not (lhs == rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are not equal
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__notequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator< [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than
Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than another JSON value rhs according to the following rules:
- If lhs and rhs have the same type, the values are compared using the default
<operator. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison
- In case lhs and rhs have different types, the values are ignored and the order of the types is considered, see operator<(const value_t, const value_t).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__less}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator< [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than
comparison: less than Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than another JSON value rhs according to the following rules:
- If lhs and rhs have the same type, the values are compared using the default
<operator. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison
- In case lhs and rhs have different types, the values are ignored and the order of the types is considered, see operator<(const value_t, const value_t).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__less}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator< [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than
comparison: less than Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than another JSON value rhs according to the following rules:
- If lhs and rhs have the same type, the values are compared using the default
<operator. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison
- In case lhs and rhs have different types, the values are ignored and the order of the types is considered, see operator<(const value_t, const value_t).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__less}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator<< [1/2]
|
friend |
deserialize from stream
- Deprecated:
- This stream operator is deprecated and will be removed in version 4.0.0 of the library. Please use operator>>(std::istream&, basic_json&) instead; that is, replace calls like
j << i;withi >> j;.
- Since
- version 1.0.0; deprecated since version 3.0.0
◆ operator<< [2/2]
|
friend |
serialize to stream
Serialize the given JSON value j to the output stream o. The JSON value will be serialized using the dump member function.
- The indentation of the output can be controlled with the member variable
widthof the output stream o. For instance, using the manipulatorstd::setw(4)on o sets the indentation level to4and the serialization result is the same as callingdump(4). - The indentation character can be controlled with the member variable
fillof the output stream o. For instance, the manipulator ‘std::setfill(’\t')` sets indentation to use a tab character rather than the default space character.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] o stream to serialize to [in] j JSON value to serialize
- Returns
- the stream o
- Exceptions
-
type_error.316 if a string stored inside the JSON value is not UTF-8 encoded
@complexity Linear.
@liveexample{The example below shows the serialization with different parameters to width to adjust the indentation level.,operator_serialize}
- Since
- version 1.0.0; indentation character added in version 3.0.0
◆ operator<= [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than or equal
Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (rhs < lhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greater}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator<= [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than or equal
comparison: less than or equal Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (rhs < lhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greater}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator<= [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: less than or equal
comparison: less than or equal Compares whether one JSON value lhs is less than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (rhs < lhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is less than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greater}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator== [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: equal
Compares two JSON values for equality according to the following rules:
- Two JSON values are equal if (1) they are from the same type and (2) their stored values are the same according to their respective
operator==. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison. Note that two NaN values are always treated as unequal.
- Two JSON null values are equal.
- Note
- Floating-point inside JSON values numbers are compared with
json::number_float_t::operator==which isdouble::operator==by default. To compare floating-point while respecting an epsilon, an alternative comparison function could be used, for instanceOr you can self-defined operator equal function like this:{}const auto lhs_type lhs.type();const auto rhs_type rhs.type();if (lhs_type == rhs_type) {switch(lhs_type)// self_defined casecase value_t::number_float:return std::abs(lhs - rhs) <= std::numeric_limits<float>::epsilon();// other cases remain the same with the original...}...} - NaN values never compare equal to themselves or to other NaN values.
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are equal
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@complexity Linear.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__equal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator== [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: equal
comparison: equal Compares two JSON values for equality according to the following rules:
- Two JSON values are equal if (1) they are from the same type and (2) their stored values are the same according to their respective
operator==. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison. Note that two NaN values are always treated as unequal.
- Two JSON null values are equal.
- Note
- Floating-point inside JSON values numbers are compared with
json::number_float_t::operator==which isdouble::operator==by default. To compare floating-point while respecting an epsilon, an alternative comparison function could be used, for instanceOr you can self-defined operator equal function like this:{}const auto lhs_type lhs.type();const auto rhs_type rhs.type();if (lhs_type == rhs_type) {switch(lhs_type)// self_defined casecase value_t::number_float:return std::abs(lhs - rhs) <= std::numeric_limits<float>::epsilon();// other cases remain the same with the original...}...} - NaN values never compare equal to themselves or to other NaN values.
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are equal
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@complexity Linear.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__equal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator== [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: equal
comparison: equal Compares two JSON values for equality according to the following rules:
- Two JSON values are equal if (1) they are from the same type and (2) their stored values are the same according to their respective
operator==. - Integer and floating-point numbers are automatically converted before comparison. Note that two NaN values are always treated as unequal.
- Two JSON null values are equal.
- Note
- Floating-point inside JSON values numbers are compared with
json::number_float_t::operator==which isdouble::operator==by default. To compare floating-point while respecting an epsilon, an alternative comparison function could be used, for instanceOr you can self-defined operator equal function like this:{}const auto lhs_type lhs.type();const auto rhs_type rhs.type();if (lhs_type == rhs_type) {switch(lhs_type)// self_defined casecase value_t::number_float:return std::abs(lhs - rhs) <= std::numeric_limits<float>::epsilon();// other cases remain the same with the original...}...} - NaN values never compare equal to themselves or to other NaN values.
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether the values lhs and rhs are equal
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@complexity Linear.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__equal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator> [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than
Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than another JSON value by calculating not (lhs <= rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__lessequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator> [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than
comparison: greater than Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than another JSON value by calculating not (lhs <= rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__lessequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator> [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than
comparison: greater than Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than another JSON value by calculating not (lhs <= rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__lessequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator>= [1/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than or equal
Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (lhs < rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greaterequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator>= [2/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than or equal
comparison: greater than or equal Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (lhs < rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greaterequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator>= [3/3]
|
friend |
comparison: greater than or equal
comparison: greater than or equal Compares whether one JSON value lhs is greater than or equal to another JSON value by calculating not (lhs < rhs).
- Parameters
-
[in] lhs first JSON value to consider [in] rhs second JSON value to consider
- Returns
- whether lhs is greater than or equal to rhs
@complexity Linear.
@exceptionsafety No-throw guarantee: this function never throws exceptions.
@liveexample{The example demonstrates comparing several JSON types.,operator__greaterequal}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ operator>> [1/2]
|
friend |
serialize to stream
- Deprecated:
- This stream operator is deprecated and will be removed in future 4.0.0 of the library. Please use operator<<(std::ostream&, const basic_json&) instead; that is, replace calls like
j >> o;witho << j;.
- Since
- version 1.0.0; deprecated since version 3.0.0
◆ operator>> [2/2]
|
friend |
deserialize from stream
Deserializes an input stream to a JSON value.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] i input stream to read a serialized JSON value from [in,out] j JSON value to write the deserialized input to
- Exceptions
-
parse_error.101 in case of an unexpected token parse_error.102 if to_unicode fails or surrogate error parse_error.103 if to_unicode fails
@complexity Linear in the length of the input. The parser is a predictive LL(1) parser.
- Note
- A UTF-8 byte order mark is silently ignored.
@liveexample{The example below shows how a JSON value is constructed by reading a serialization from a stream.,operator_deserialize}
- See also
- parse(std::istream&, const parser_callback_t) for a variant with a parser callback function to filter values while parsing
- Since
- version 1.0.0
◆ swap
exchanges the values
Exchanges the contents of the JSON value from left with those of right. Does not invoke any move, copy, or swap operations on individual elements. All iterators and references remain valid. The past-the-end iterator is invalidated. implemented as a friend function callable via ADL.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] left JSON value to exchange the contents with [in,out] right JSON value to exchange the contents with
@complexity Constant.
@liveexample{The example below shows how JSON values can be swapped with swap().,swap__reference}
- Since
- version 1.0.0
Field Documentation
◆ __pad0__
|
private |
◆ __pad1__
|
private |
◆ __pad2__
|
private |
◆ __pad3__
| JSON_PRIVATE_UNLESS_TESTED nlohmann::basic_json::__pad3__ |
◆ array
|
private |
array (stored with pointer to save storage)
Definition at line 18360 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by create_map_in_quest_array(), create_maps_array(), create_region_array(), destroy(), fill_json(), init_renderer_env(), and json_value().
◆ binary
|
private |
binary (stored with pointer to save storage)
Definition at line 18364 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by destroy(), and json_value().
◆ boolean
◆ m_value
| json_value nlohmann::basic_json::m_value = {} |
the value of the current element
Definition at line 24563 of file json.hpp.
Referenced by assert_invariant(), at(), basic_json(), clear(), contains(), count(), emplace(), emplace_back(), empty(), erase(), find(), get_impl(), get_impl_ptr(), insert(), insert_iterator(), max_size(), operator=(), operator[](), patch(), push_back(), set_parent(), set_parents(), size(), swap(), update(), and ~basic_json().
◆ number_float
|
private |
◆ number_integer
|
private |
◆ number_unsigned
|
private |
◆ string
|
private |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- crossfire-crossfire-server/utils/mapper/nlohmann/json.hpp